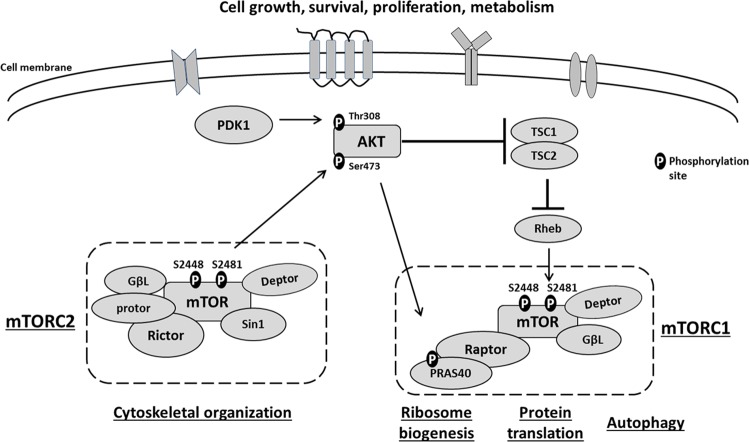
Fig. 1. AKT-mTOR signaling pathway.
AKT and mTOR are key kinases in this signaling cascade. They both require phosphorylation for complete activation. mTOR forms two distinct complexes: mTORC1 and mTORC2. mTORC1 comprises of mTOR, Raptor, Deptor, PRAS40, and GβL, and facilitates ribosome biogenesis, protein translation and autophagy. mTORC2 consists of mTOR, Rictor, Deptor, Protor, GβL, and Sin1, and modulates cytoskeleton organization. AKT is functionally interconnected with mTOR complexes since it positively regulates mTORC1 activity via Rheb, whereas mTORC2 positively regulates AKT activity by phosphorylating it at S473.