FIG 4.
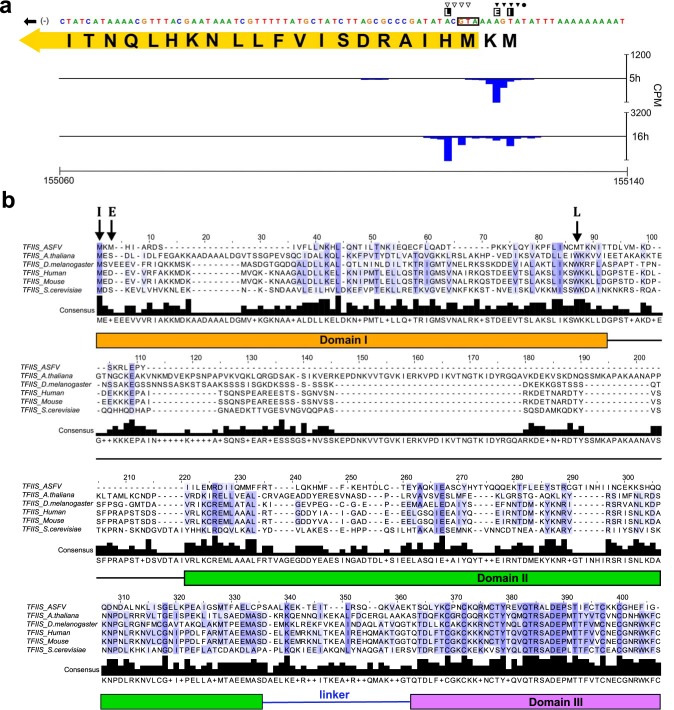
Analysis of alternative pTSS usage in I243L. (a) Close-up of TSSs (CAGE-seq alignments) on the minus strand at the start of the I243L ORF. Symbols indicate the TSS sites for early (▼), intermediate (•), and late (▽) gene expression according to Rodríguez et al. (26), while E, I, and L indicate, respectively, early, intermediate, and late gene pTSS positions concluded from our data. The first 21 aa residues of the annotated I243L ORF are shown; in yellow is the reannotated ORF which could be encoded in transcripts initiating from both of our annotated early pTSSs. (b) ClustalW multiple-sequence alignment colored by percentage identity between sequences at the same position from white (0%) to blue (100%), according to their agreement with the consensus sequence found below the alignment ('+' indicates positions where more than one residue is found in the modal consensus), illustrated with Jalview (84), of TFIIS homologues from ASFV (I243L; NCBI accession no. P27948), Arabidopsis thaliana (Q9ZVH8), Drosophila melanogaster (P20232), human (P23193), mouse (P10711), and Saccharomyces cerevisiae (P07273). S. cerevisiae TFIIS domain locations according to Kettenberger et al. (85) are shown below the alignment, and acidic (DE) catalytic residues are in domain III. ASFV-TFIIS start codons encoded from alternative transcription start sites are labeled as in panel a.