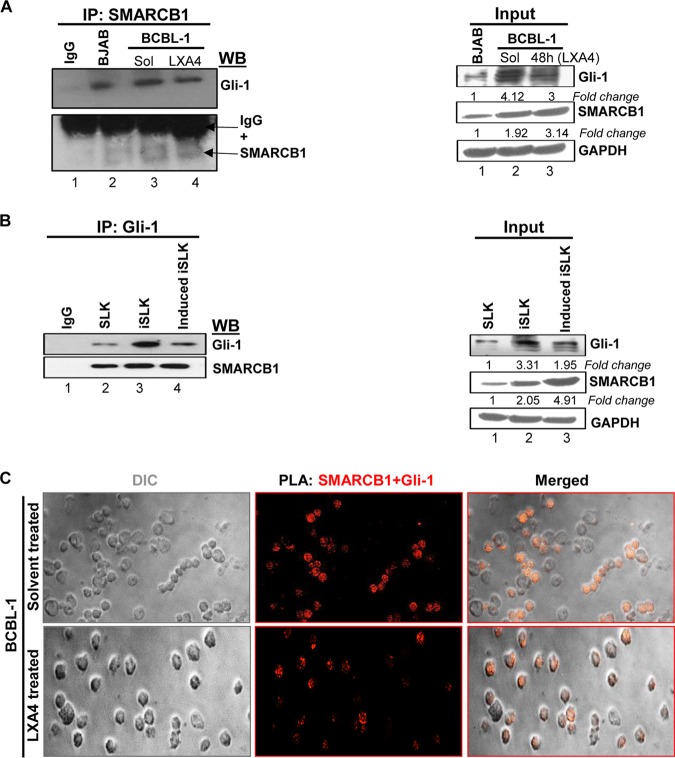
FIG 7.
SMARCB1 interacts with Gli-1 in KSHV-infected cells (A) (Left) Immunoprecipitation (IP) assay. BCBL-1 cells treated with solvent or LXA4 (48 h) and BJAB cells (KSHV and EBV negative) were harvested, and the lysates were precipitated with SMARCB1 and analyzed by immunoblotting with Gli-1 and SMARCB1. (Right) The input for the left panel. Representative data from three experiments are shown here. (B) (Left) Immunoprecipitation assay using SLK, iSLK, and induced iSLK cells. The cells were harvested, and the lysates were precipitated with Gli-1 and analyzed by immunoblotting with Gli-1 and SMARCB1. (Right) The input for the left panel. Representative data from three experiments are shown here. (C) Proximity ligation assay (PLA) to detect the interaction between SMARCB1 and Gli-1. BCBL-1 cells treated with solvent or LXA4 were washed, fixed, permeabilized, and reacted with SMARCB1 and Gli-1 primary antibodies, followed by PLA to assess the interactions between SMARCB1 and Gli-1. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. The differential interference contrast (DIC) image shown in the merged panels corresponds to the fluorescence image. The PLA reaction was detected using the Duolink red detection agent. Red puncta in the nucleus indicate a positive PLA signal, suggesting interactions between the two proteins. Images were captured at a ×40 magnification.