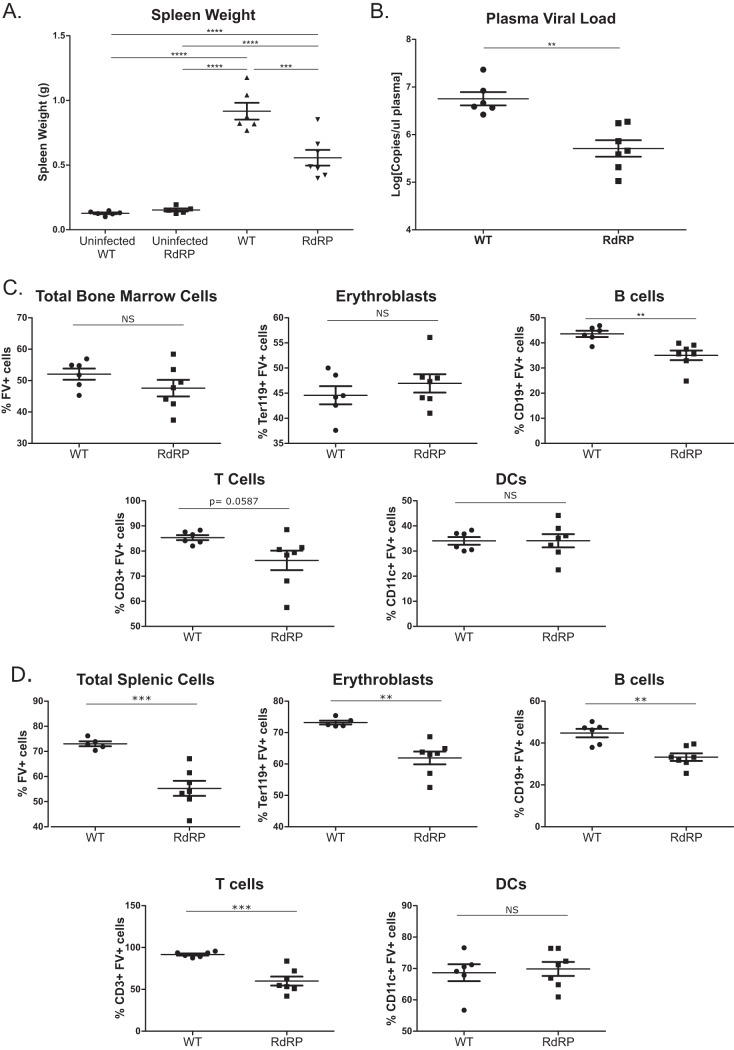
FIG 1.
Differences in high-dose acute phase FV infection in WT and RdRP mice. Mixed-gender, 13- to 16-week-old mice were infected with 10,000 PFU B-tropic FV by retroorbital injection. (A) At 7 dpi, spleens were harvested for weight analysis to determine the level of splenomegaly. (B) Plasma was simultaneously obtained to determine plasma viral load via qPCR. (C) Bone marrow was harvested, and a single-cell suspension was created to determine the overall amount of FV infection, as well as the level of FV infection in erythroblasts, B cells, T cells, and DCs via flow cytometry. (D) As in panel C, single-cell solutions were prepared from spleen, and the overall infection level, as well as infection of erythroblasts, B cells, T cells, and DCs, was determined using flow cytometry. For all experiments shown, n = 6 for WT uninfected and WT, n = 5 for RdRP uninfected, and n = 7 for RdRP. A one-way ANOVA with a Tukey test was used to analyze data in panel A, and student’s t tests were used to analyze data in panels B through D. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001. Data in panel B were log transformed prior to statistical analysis.