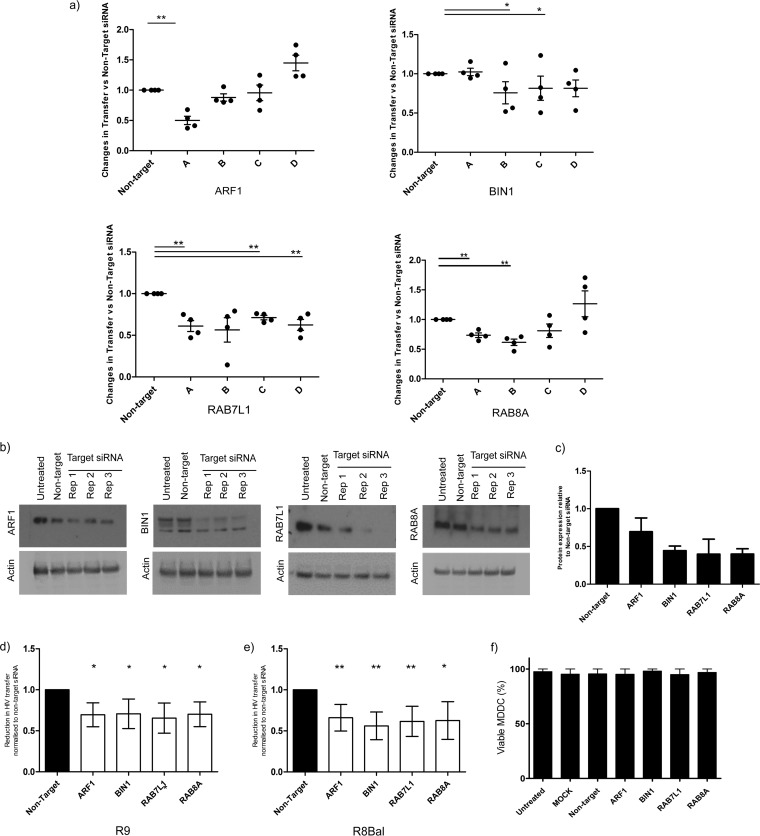
FIG 2.
ARF1, BIN1, RAB7L1, and RAB8A regulate HIV trans-infection in DCs and T cells. (a) Validation of siRNA knockdown on trans-infection against four individual siRNAs from each candidate gene. The percentage of HIV-1 transfer is normalized to nontarget siRNA set at a value of 1.0. Each point represents an individual donor. The means ± the SD are shown. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.005. (b) Western blot analysis of pooled siRNA knockdown in MDDCs at 72 h posttransfection with ARF1, BIN1, RAB7L1, and RAB8A siRNA performed in triplicate in untreated MDDCs and non-target siRNA. Actin is used as a loading control. (c) Densitometry quantification of protein expression levels for ARF1, BIN1, RAB7L1, and RAB8A. The protein expression levels for siRNA-transfected MDDCs were normalized to an actin loading control. All values are relative to nontarget siRNA-transfected lanes (set at 1.0). The means ± the SD are shown (n = 3). (d) Effects of final target siRNA on HIV-1 trans-infection with CXCR4 (R9). The reduction in viral transfer was measured relative to nontarget siRNA. The means and SD are shown for each sample (n = 5). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.005. (e) Effects of final target siRNA on HIV-1 trans-infection with CCR5 (R8Bal). The reduction in viral transfer was measured relative to nontarget siRNA. The means and SD are shown for each sample (n = 5). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.005. (f) The effects of ARF1, BIN1, RAB7L1, and RAB8A siRNA transfection on the viability of MDDCs at 48 h posttransfection. All samples compared to untreated MDDCs. Cell viability is shown as a percentage. The means ± the SD are shown (n = 2).