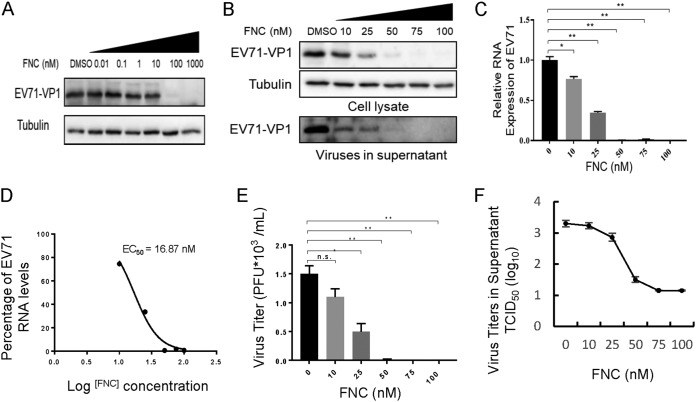
FIG 3.
FNC potently inhibits the replication of EV71 in a dose-dependent manner. (A and B) Inhibitory effect of FNC on EV71 replication in the 0.01 to 1,000 nM (A) or 10 to 100 nM (B) dose range. RD cells were infected with EV71 as described in Fig. 2B, and the indicated concentration of FNC was added to RD cells for 48 h. The cells were then harvested for WB analysis. The supernatant from the infected RD was centrifuged and then loaded for WB analysis. Tubulin was used as a loading control. (C) Cellular EV71 RNA levels in panel B were detected by RT-qPCR. GAPDH was used as a control. The EV71 RNA level without FNC treatment was set as 100%. (D) The EC50 of FNC was calculated according to panel C using GraphPad Prism7. (E and F) Viral titers in the supernatants from the experiment shown in panel B were determined by the plaque assay (E) and by the cytopathic effect (CPE) method (F). The results shown are the means with SDs from two independent experiments. The asterisks indicate statistically significant differences between groups, as assessed by Student's t test (*, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01; and ***, P ≤ 0.001; ns, not significant).