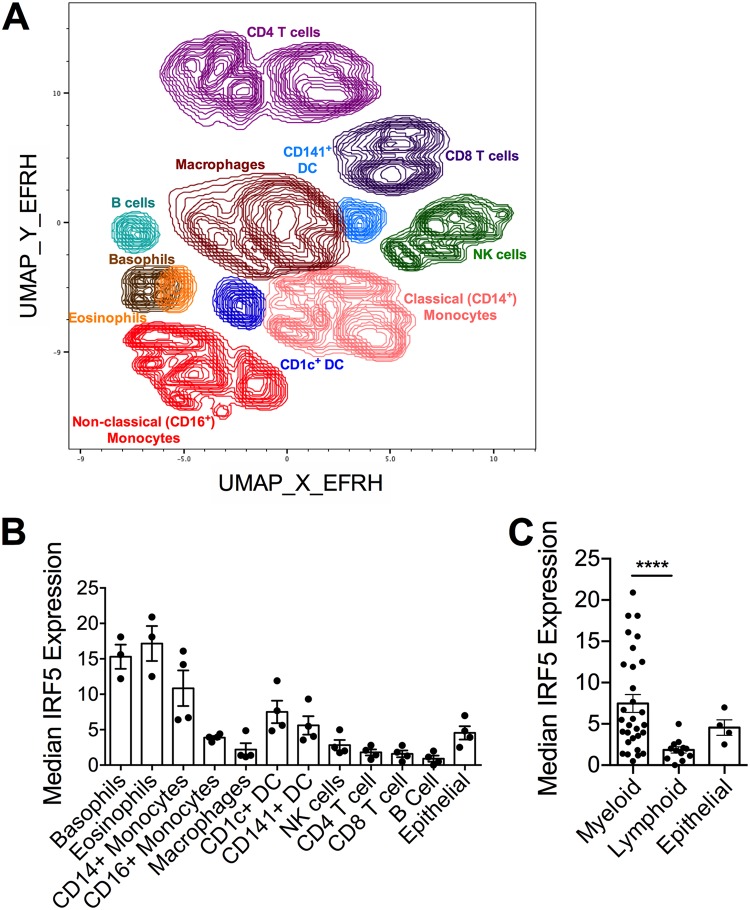
FIG 3.
IRF5 expression in human lung cells. IRF5 expression by multiple cellular subsets derived from human lung tissue from independent donors was analyzed by CyTOF. (A) UMAP based on downsampled, concatenated files from lung samples from four donors using phenotypic markers. Post-UMAP analysis, populations (colored by cell type as identified by lung CyTOF) were defined via the following markers: CD4+ T cells, CD3+ CD4+ CD20−; CD8+ T cells, CD3+ CD20− CD8+; B cells, CD3− CD20+; NK cells, CD3− CD20− CD56+; CD14+ monocytes, CD16− CD11b+ CD14+ HLA-DR+; CD16+ monocytes, CD14− CD11b+ CD16+ HLA-DR+; macrophages, CD11b+ CD68+ HLA-DR+; pDCs, CD123+ CD11b+ HLA-DR+; CD141+ cDCs, CD11b+ HLA-DR+ CD1c− CD141+; CD1c+ cDCs, CD11b+ HLA-DR+ CD1c+ CD141−; eosinophils, Siglec8+ CD123−; and basophils, Siglec8+ CD123+. (B) Median IRF5 expression in populations identified in panel A from lung samples taken from four independent donors, corrected for nonspecific staining using unpermeabilized controls for each sample, and error bars represent the SEM. (C) Median IRF5 expression in myeloid versus lymphoid cell subsets, and error bars represent the SEM.