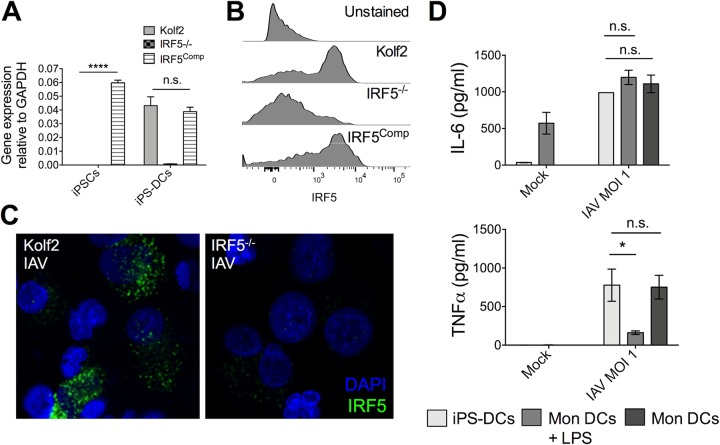
FIG 4.
IRF5−/− iPSCs, IRF5Comp iPSCs, and Kolf2 iPSCs can be differentiated into iPS-DCs which lack or express IRF5. CRISPR-Cas9 was used to generate biallelic mutations in IRF5 in the Kolf2 background. IRF5Comp iPSCs were generated using TALEN-mediated integration of IRF5 into the IRF5−/− background. (A) Relative expression of IRF5 in iPSCs and iPS-DCs relative to GAPDH. Data are shown as four technical replicates per assay, with assays repeated three times from independent iPS-DC batches. (B) Flow cytometry showing IRF5 expression in iPS-DCs generated from IRF5−/−, IRF5Comp, and Kolf2 iPSCs. (C) Immunostaining for IRF5 in A/X-31 influenza (IAV)-infected Kolf2 and IRF5−/− iPS-DCs (DAPI, blue; IRF5, green). (D) IL-6 and TNF-α production 24 h p.i. by IAV-challenged Kolf2 iPS-DCs and monocyte-derived DCs generated from human peripheral blood, either with or without 48 h LPS maturation, were assayed by ELISA. Data represented show the mean ± SEM from three independent Kolf2 differentiations for iPS-DCs, and from three independent healthy donors for monocyte-derived DCs.