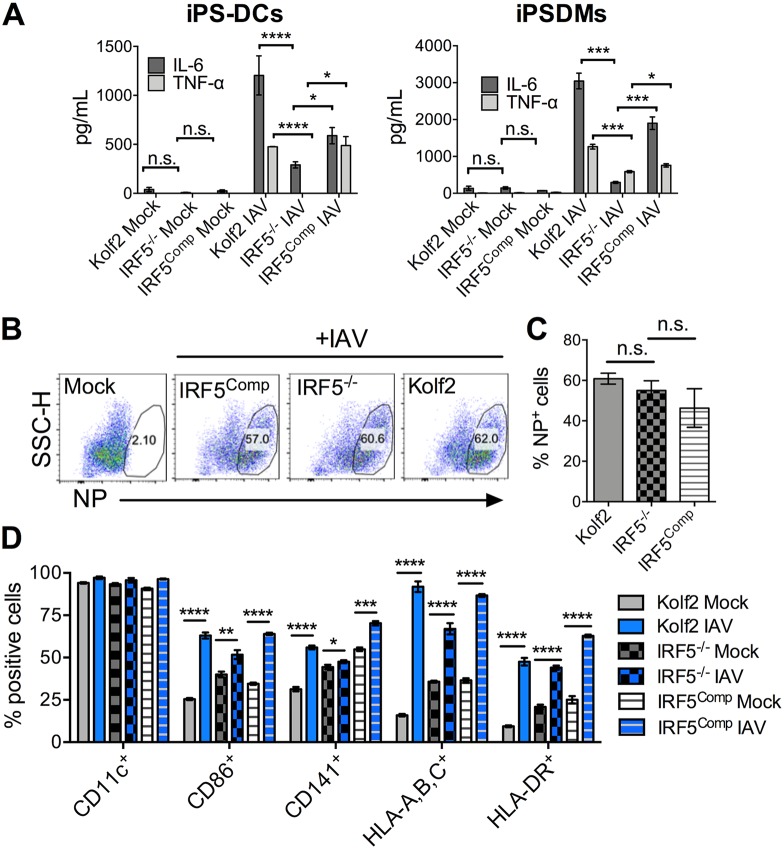
FIG 6.
IRF5 enhances IAV-induced inflammatory cytokine production in iPS-DCs and iPSDMs. (A) IL-6 and TNF-α were measured by ELISA in supernatants harvested from iPS-DCs and iPSDMs generated from an iPSC line with a biallelic mutation in IRF5, compared to the parent line Kolf2, and a line with a functional IRF5 gene was reintroduced into the AAVS1 integration site by TALEN engineering after infection with IAV at an MOI of 1. Supernatants were harvested at 24 h for assays; data shown represent the mean ± SEM for triplicate wells from at least 3 independent experiments. (B) IRF5−/−, IRF5Comp, and Kolf2 iPS-DCs were infected with IAV at an MOI of 1 and then stained for IAV NP 24 h postinfection and analyzed via flow cytometry. SSC-H, side scatter height. (C) Percentage of positive NP iPS-DCs 24 h postinfection with IAV, with data presented showing the mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. (D) Expression of DC maturation surface markers for iPS-DCs generated from IRF5−/−, Kolf2, or IRF5Comp hIPSCs 24 h postinfection with A/X-31 influenza (IAV) at an MOI of 1, as measured by flow cytometry, with data presented showing the mean ± SEM from three independent experiments.