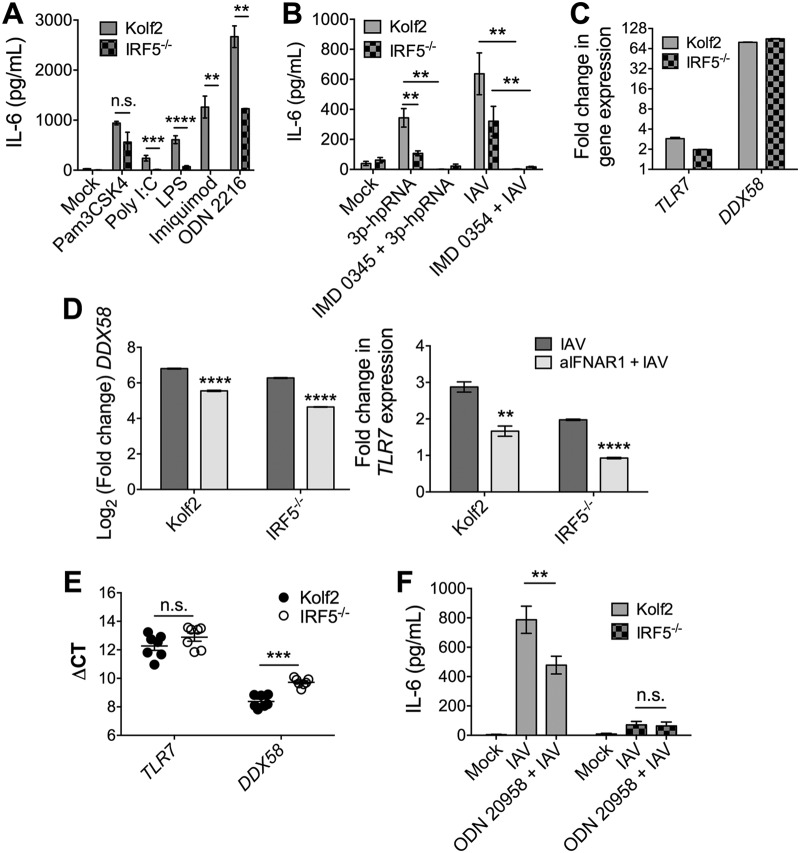
FIG 8.
IRF5 acts downstream of TLR7 and RIG-I to drive inflammatory cytokine responses in iPS-DCs. A total of 2 × 104 iPS-DCs were challenged as stated below for each condition in each assay, and supernatants were harvested after 24 h. A/X-31 influenza virus (IAV) was used at an MOI of 1. For blocking assays, cells were either preincubated for 1 h with inhibitor (IMD 0354, IKKβ inhibitor), or inhibitor was added directly with viral inoculum (ODN 20958, TLR7 inhibitor). Data shown represent the mean ± SEM of the results for triplicate wells from at least 3 experiments, unless otherwise stated. (A) IL-6 production by Kolf2 and IRF5−/− iPS-DCs in response to stimulation with various TLR ligands (TLR2, Pam3CSK4, 300 ng/ml; TLR3, poly(I·C), 50 μg/ml; TLR4, LPS, 50 μg/ml; TLR7, imiquimod, 50 μg/ml; TLR9, ODN 2216, 3 μg/ml) was measured by ELISA. Data shown represent four wells per condition for one iPS-DC batch per line, with assays replicated in two independent experiments. (B) IL-6 response as measured by ELISA in Kolf2 and IRF5−/− iPS-DCs to RIG-I ligand 3p-hpRNA with or without IKKβ inhibitor IMD 0354 and to IAV with or without IMD 0354. (C) Fold change in mRNA levels for TLR7 and DDX58, measured by RT-qPCR using GAPDH as an endogenous control. (D) DDX58 and TLR7 mRNA levels in iPS-DCs after IAV infection with or without blocking of type I IFN signaling using anti-IFNAR1. Data shown represent four technical replicates per assay, with assays repeated at least twice from independent iPS-DC batches. (E) Relative mRNA levels of TLR7 in iPS-DCs generated from IRF5−/− iPSCs or parent Kolf2 iPSCs, measured using RT-qPCR. (F) IL-6 response as measured by ELISA in Kolf2 and IRF5−/− iPS-DCs to A/X-31 influenza virus with or without TLR7 inhibitor ODN 20958.