Figure 3.
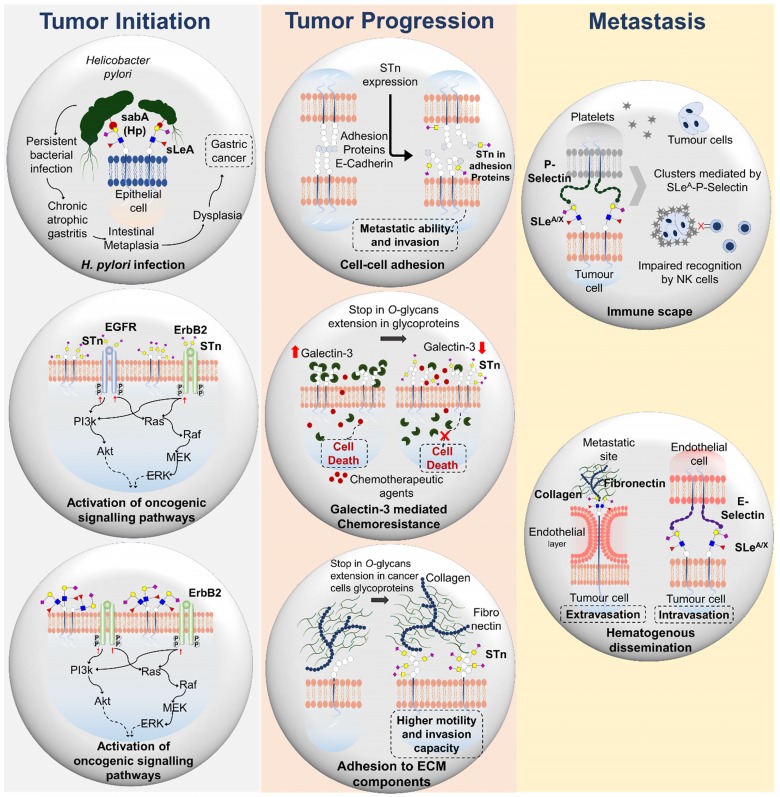
Functional impact of STn and SLeA expression in gastrointestinal tumors. Both STn and SLeA overexpression influence tumor initiating processes as constitutive activation of several oncogenic signalling mediate by EGFR and ErbB2. Moreover, SLeA also facilitates H. pylori adhesion to the gastric epithelium, contributing to persistent infection and potentially cancer development. STn also drives tumor progression by negatively impacting cell-cell and cell-extracellular matrix adhesion as well as galectin-3-mediated chemoresistance. Moreover, sialylated lewis antigens facilitate hematogenous metastasis of tumor cells through E-selectin interactions, while protecting tumor cells from sheer stress in circulation and hampering immune recognition.