Figure 4.
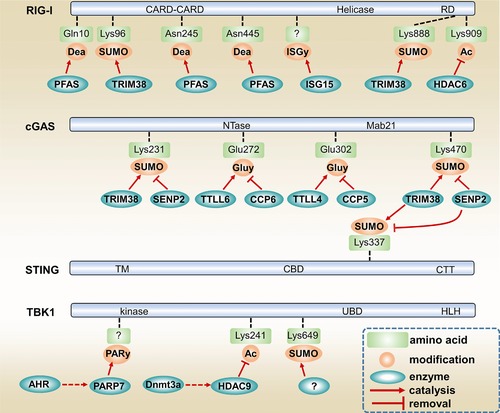
Non‐canonical PTMs of RIG‐I, cGAS, STING and TBK1. RIG‐I is deamidated by PFAS at Q10, N245 and N445. RIG‐I's deamidation is crucial for RIG‐I signaling during γHV68 infection. TRIM38 promotes RIG‐I activation by inducing RIG‐I SUMOylation at K96 and K888. ISG15 limits RIG‐I activation by catalyzing RIG‐I ISGylation. HDAC6 is critical for RIG‐I activation by removing RIG‐I K909 acetylation. TRIM38 also promotes cGAS signaling by catalyzing cGAS K231 and K470 SUMOylation as well as STING K337 SUMOylation. SENP2 inhibits cGAS signaling by counteracting TRIM38‐mediated SUMOylation of cGAS and STING. AHR signaling moderates antiviral response by promoting PARP7‐mediated TBK1 ADP‐ribosylation. Dnmt3a contributes to IFN‐β production by promoting HDAC9 expression. HDAC9 removes TBK1 K241 acetylation to boost TBK1 kinase activity. Dea, deamidation. SUMO, SUMOylation. ISGy, ISGylation. Ac, acetylation. Gluy, glutamylation. PARy, ADP‐ribosylation. CARD, caspase recruitment domain. RD, regulatory domain. Mab21, Mab‐21 domain. TM, transmembrane domain. CBD, c‐di‐GMP binding domain. CTT, c‐terminal tail. UBD, ubiquitin‐binding domain. HLH, helix‐loop‐helix domain.
