Fig. 3.
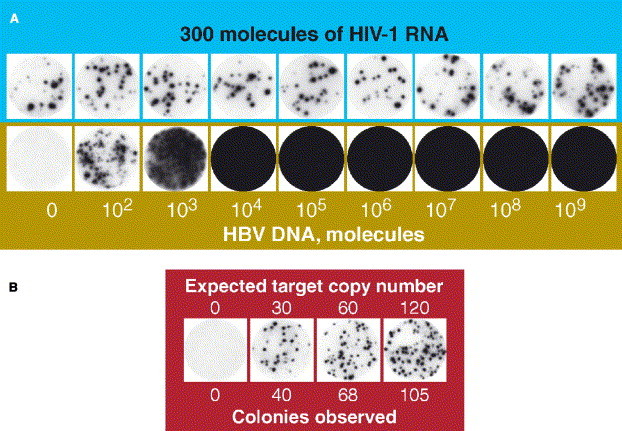
Assay of RNA and DNA targets with the PCR version of the molecular colony technique. A: Lack of competition between targets in a multiplex assay. Colonies produced by 300 molecules of human immunodeficiency virus type-1 (HIV-1) RNA in the presence of the indicated number of concurrently amplifying molecules of human hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA. Each of the nine gels was blotted with a nylon membrane that was first hybridized with an HIV-1-specific 32P-labeled probe (top row) and then with an HBV-specific probe (bottom row). B: Detection of HBV DNA molecules in human blood. Total nucleic acids were isolated from 60-μl aliquots of the whole human blood to which diluted samples, expected to contain the indicated number of HBV DNA molecules, had been added. The blood aliquots contained nucleic acids equivalent by weight to 1013 molecules of the target. (Reprinted from [55] by permission of BioTechniques/Eaton Publishing.)
