Figure 1.
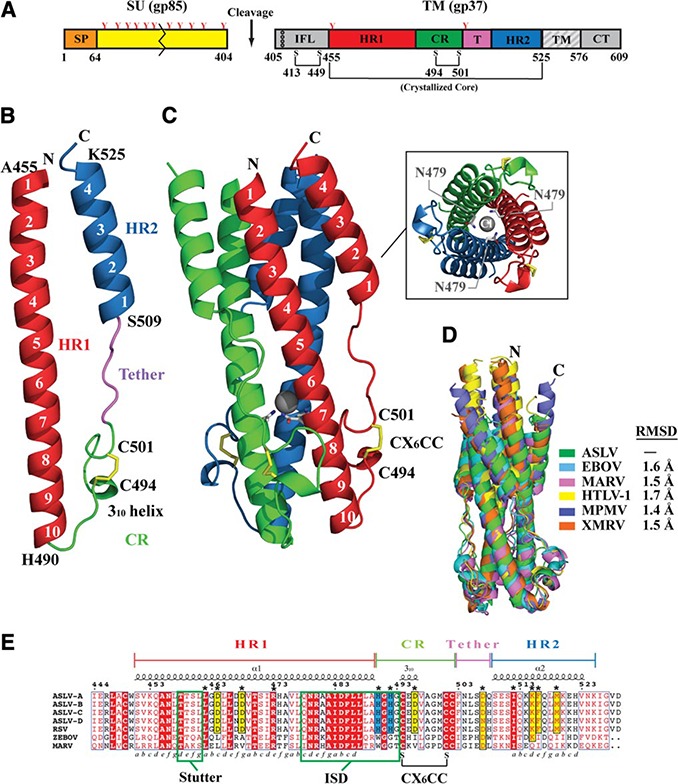
Structure of ASLV TM. A) Schematic of the ASLV Env. CR, chain reversal region; CT, cytoplasmic tail; HR1, heptad repeat 1 region; HR2, heptad repeat 2 region; IFL, internal fusion loop; SP, signal peptide; SU, surface attachment subunit; TM, transmembrane domain. Colored regions correspond to the ASLV TM core that was crystallized. Red Y‐shaped symbols denote N‐linked glycans. TM fusion subunit contains 3 disulfide linkages: one within the hydrophobic internal fusion loop, one in the chain‐reversal region, and an intermolecular covalent linkage between the SU and TM. B) Monomer of the ASLV TM. Features in the TM are color coded to the regions shown in panel A. C) Trimeric ASLV TM postfusion peplomer. The 3 ASLV TM monomers are shown in red, blue, and green. Inset: view of ASLV TM down the 3‐fold axis, showing the chloride ion bound by 3 aspargine residues within the inner HR1 core. D) Structural superimposition of ASLV TM and other retroviral and filoviral fusion subunits. PDB coordinate files used are as follows: ASLV, 4JPR; EBOV, 2EBO; MARV, 4G2K; HTLV‐1, 1MG1; MPMV, 4JF3; XMRV, 4JGS. E) Primary sequence alignment of ASLV TM subtypes A–D, Rous sarcoma virus (RSV) TM, EBOV GP2, and MARV GP2. The 3–4 periodicity of the HRs is shown below the alignment. Stutter region, immunosuppressive domain (ISD), and CX6CC motif are highlighted within labeled green boxes.
