Figure 7.
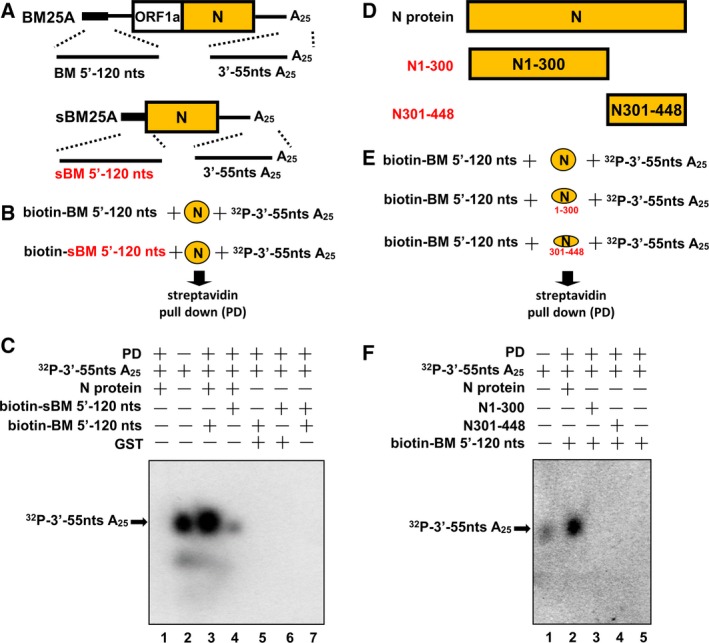
Interaction between the 5′‐ and 3′‐ends of the genome mediated by the N protein. (A) Schematic diagram depicting the sequences located at the 5′‐ and 3′‐termini of the CoV DI RNA genome (BM25A) and N subgenome (sBM25A) used for evaluating crosstalk between the two ends mediated by the N protein. (B) Diagram showing the strategy for assessing interaction between the 5′‐ and 3′‐ends of the genome and N subgenome. A biotin‐labeled 5′‐terminal RNA was incubated with N protein and 3′‐terminal 32P‐labeled RNA followed by a streptavidin pull‐down assay and RNA extraction. (C) Detection of 32P‐labeled RNA (indicated by arrow) by 6% denaturing gel electrophoresis to determine interaction between the two ends of the genome and N subgenome. (D) Schematic diagrams depicting the structure of BCoV N protein and its mutants N1–300 (N protein amino acids 1–300) and N301–448 (N protein amino acids 301–448). (E) Diagram showing the strategy for assessing the domains in N protein responsible for the interaction between the 5′‐ and 3′‐ends of the genome. (F) Detection of 32P‐labeled RNA (indicated by arrow) by 6% denaturing gel electrophoresis to identify the domain in N protein involved in the interaction between the 5′‐ and 3′‐ends of the genome. PD, pull‐down.
