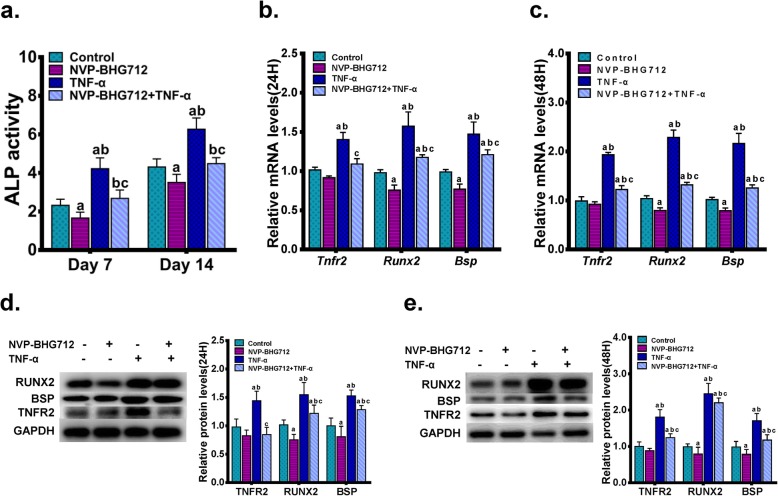
Fig. 5.
The effect of inhibited EphB4 forward signaling on TNF-α-stimulated TNFR2 expression and osteogenic differentiation. (a) A potent inhibitor of EphB4 auto-phosphorylation, NVP-BHG712, was used to suppress EphB4 forward signaling. MC3T3-E1 cells were pretreated with 200 nM NVP-BHG712 in the regular culture medium for 1 h. Cells were then incubated in osteogenic induction medium supplemented with 200 nM NVP-BHG712 and/or 0.5 ng/ml TNF-α for 7d or 14d. MC3T3-E1 cells cultured in osteogenic induction medium served as controls. The ALP activities were determined. (b, c) MC3T3-E1 cells were pretreated with 200 nM NVP-BHG712 for 1 h in the regular culture medium, and then incubated in osteogenic induction medium supplemented with 200 nM NVP-BHG712 and/or 0.5 ng/ml TNF-α. Cells cultured in osteogenic induction medium served as controls. mRNA levels of Tnfr2, Runx2 and Bsp were determined after 24 h (b) or 48 h (c) of incubation. (d, e) MC3T3-E1 cells were pretreated with 200 nM NVP-BHG712 for 1 h in the regular culture medium, and then incubated in osteogenic induction medium supplemented with 200 nM NVP-BHG712 and/or 0.5 ng/ml TNF-α. Cells cultured in osteogenic induction medium served as controls. Protein levels of TNFR2, RUNX2 and BSP were determined after 24 h (d) or 48 h (e) of incubation. a, p < 0.05 vs. the control group; b, p < 0.05 vs. the NVP-BHG712 group; c, p < 0.05 vs. the TNF-α group