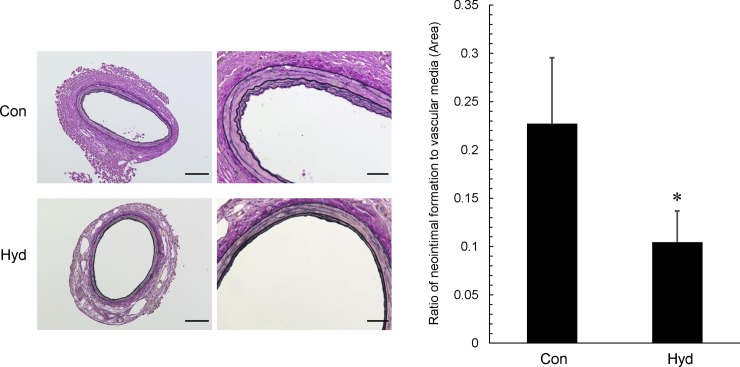
Fig 2. Effect of hydrogen gas inhalation on neointima formation in injured femoral artery after cuff placement.
After inhalation of hydrogen gas for 2 weeks from 8 weeks of age in C57BL/6 mice, cuff injury was induced by polyethylene cuff placement around the femoral artery. Representative photos and quantitative analysis of neointimal area in cross sections of femoral artery with elastic van Gieson (EVG) staining are shown. Original magnification ×200 (scale bar: 100 μm) and ×600 (scale bar: 30 μm). In quantitative analysis, data represent the ratio of neointima formation area to vascular media area, and values are mean ± SEM (n = 16 for control group (Con), n = 24 for hydrogen group (Hyd)). *p<0.05 vs. Con.