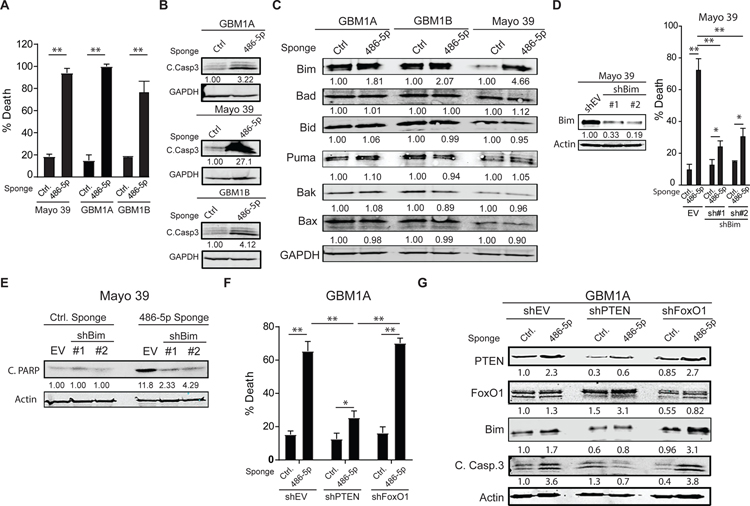
Figure 5: miR-486–5p inhibition activates Bim and induces apoptosis in GBM neurospheres.
(A) Equal numbers of GBM1A neurosphere cells transduced with lentiviral constructs expressing a miR-486–5p sponge or a control vector were cultured in neurosphere medium containing EGF/FGF for 14 days and neurosphere numbers (>100µm diameter) were quantified by computer-assisted image analysis. (B) Western blot showing cleaved caspase 3 cleavage 6 days after miR-486–5p inhibition. (C) Western blots showing expression of pro-apoptotic proteins 3 days after miR-486–5p inhibition. (D) Mayo 39 primary GBM cells were transduced with two independent shRNA hairpins targeting BIM. Western blot showing BIM levels following shRNA knock-down (right panel). Cell viability 5 days after miR-485–5p inhibition in cells transduced with shEV or shBim (right panel). (E) Western blot showing PARP cleavage 5 days after miR-485–5p inhibition in cells transduced with shEV or shBim. (F) Cell viability 5 days after miR-485–5p inhibition in cells transduced with shEV, shPTEN, or shFoxO1. (G) Western blot showing expression of PTEN, FoxO1, Bim and cleaved caspase 3 in GBM1A neurospheres after PTEN or FoxO1 knock-down and miR-486–5p inhibition. Student’s t-test was used to calculate statistical significance in panel A; Two-way ANOVA with Tuckey’s post hoc test was used calculate statistical significance in panels D and F. Data are presented as means ± S.D *p< 0.05; **p< 0.01