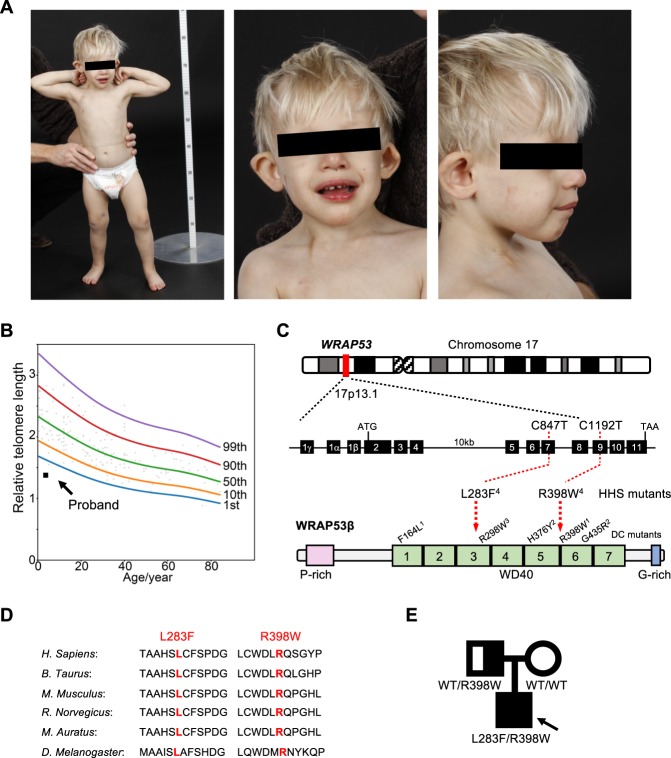
Fig. 1. Identification of missense mutations in WRAP53 in a patient with HHS.
a At an age of 2.7 years, the proband demonstrated microcephaly, short stature, broad gait, fine blond hair and dysmorphic features (including strabismus, epicanthal folds, cup-shaped protruding overfolded ears, a depressed nasal tip and widely spaced teeth). b Analysis of telomere lengths by quantitative PCR in peripheral blood leukocytes collected from the proband at this same age (solid square). The reference relative telomere length (RTL) were determined from telomere length analysis of blood leukocytes from 173 healthy subjects (0–84 years of age; open circles). The curves shown depict the first, 10th, 50th, 90th, and 99th normal percentiles at each age. c Schematic illustration of the WRAP53 gene, the protein encoded and the positions of the mutations detected in the proband. The DC mutations in WRAP53β reported previously are also marked with the superscripts indicating mutations that occur in the same patient. Note: Exon numbering is based on the GenBank sequence DQ431240, i.e., the separation of exon 1β and 2 by an intron. In the reference sequence NM 018081 this intron is included resulting in different exon numbering. d Conservation of the sites of HHS mutations (marked in red) among species. e Pedigree of the family carrying autosomal recessive HHS and mutations in WRAP53. The arrow indicates the proband. The heterozygous carrier (the father, half-filled symbol), compound heterozygous carrier (the proband, filled symbol), and wild-type individual (the mother, non-filled symbol) are shown.