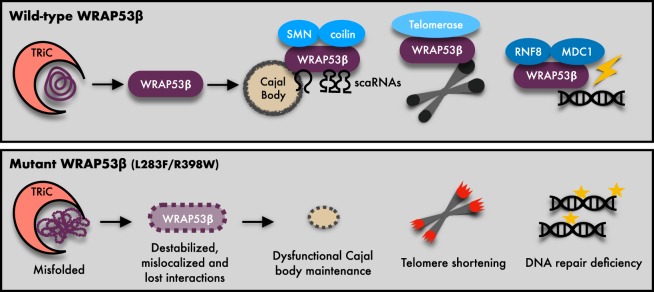
Fig. 5. Model of defects caused by HHS mutations in WRAP53.
Schematic illustrations of the normal folding and functions of wild-type (WT) WRAP53β and molecular defects and functional consequences of the HHS mutations. WRAP53 mutations results in misfolding and destabilization of the WRAP53β protein and impair the binding to and trafficking of partner proteins and RNAs to correct cellular sites. Consequently, this perturbs maintenance of Cajal bodies, shortens telomeres and impairs DNA repair, thereby causing HHS.