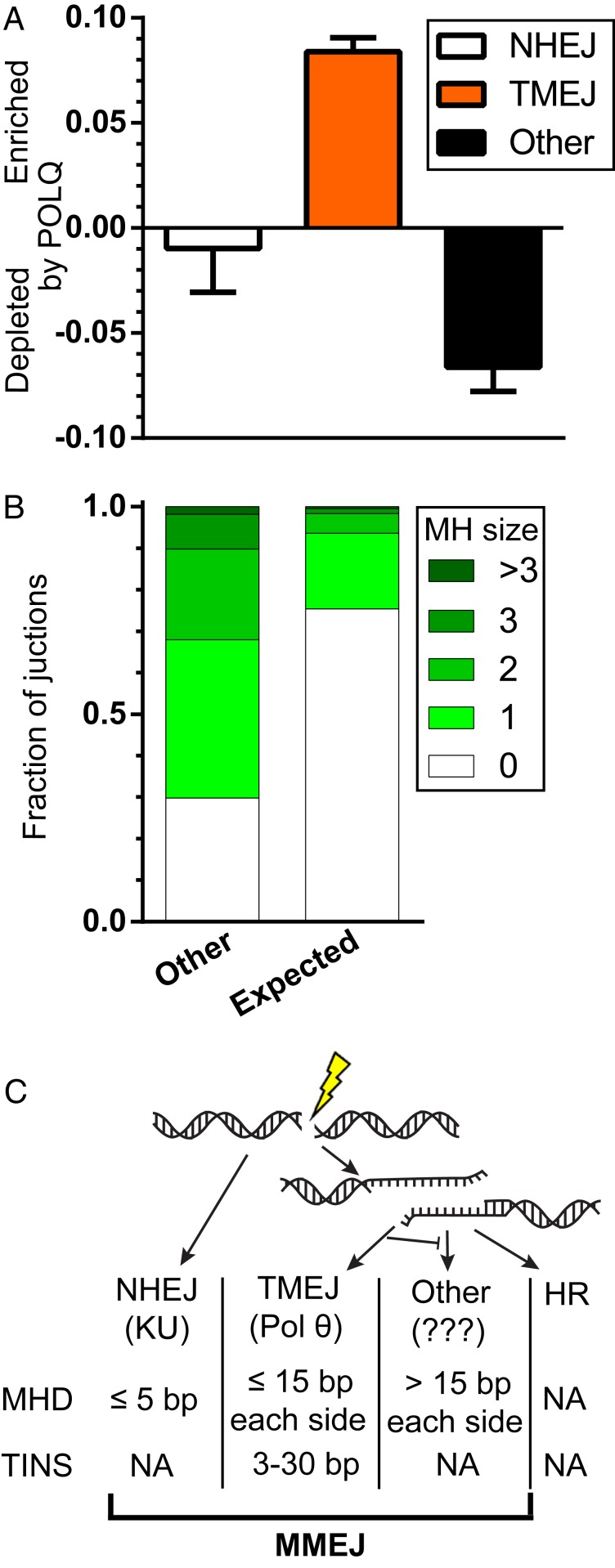
Fig. 7.
TMEJ promotes genomic stability. (A) The extent of enrichment of repair product classes upon POLQ expression, averaged across all five break sites. Products were classified as NHEJ (white bar) if deleted sequence was less than 5 bp and possessed no or 1 bp of microhomology, as TMEJ (orange bar) if deleted sequence was less than 15 from either end and possessed 2 bp or more of microhomology, or had templated insertions larger than 2 bp, and as “other” (black bar) if deleted sequence from either flank exceed 15 bp. Bar represents the mean and error bars SEM from the five loci. (B) Average fraction of repair events associated with the indicated microhomology sizes in deletions larger than 15 bp from both sides of the break (other) or as would be expected by chance, if microhomologies played no role (expected). (C) Following a DSB, ends are either ligated through the NHEJ pathway (dependent on the KU heterodimer) or resected to form 3′ ssDNA tails. These are substrates for TMEJ (dependent on Pol θ), HR, or a third, undescribed form of end joining that also favors microhomologies. Different end joining pathways have different mutational outcomes (MHD of the indicated sizes or TINS).