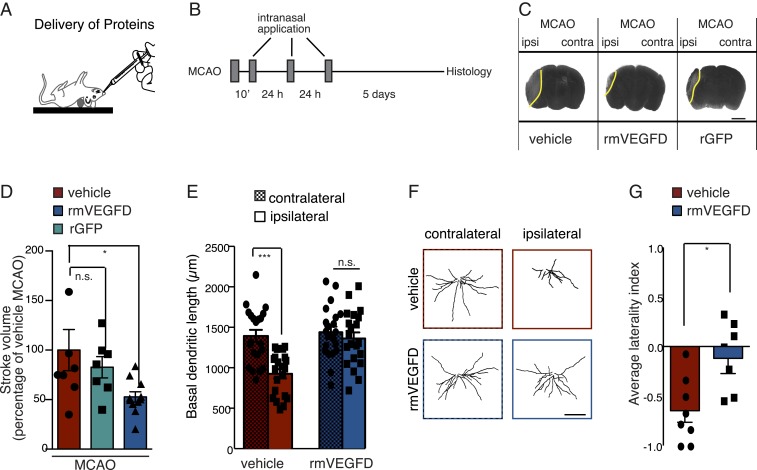
Fig. 3.
Nose-to-brain delivery of rmVEGFD prevents MCAO-induced dendrite loss and reduces brain damage. (A) Schematic illustration of intranasal protein application. (B) Timeframe of the experiment. Recombinant proteins were delivered at 10 min after MCAO to the left naris. Application was repeated at 24 h and 48 h post-MCAO. Histology was performed at 8 d post-MCAO. (C) Silver-stained coronal brain sections of mice after MCAO that received nose drops of rmVEGFD, rGFP, or vehicle. (Scale bar: 0.20 cm.) (D) Infarct volumes in brains of mice that were subjected to MCAO and received nose drops of rmVEGFD (n = 11), rGFP (n = 7), or vehicle (n = 8). (E) Length of the basal dendritic trees of layer 2/3 pyramidal neurons from the ipsilateral and contralateral cortices of mice after MCAO that received nose drops of rmVEGFD or vehicle (n = 21 neurons; 4 mice per condition). (F) Representative tracings of layer 2/3 pyramidal neurons as in E. (Scale bar: 50 µm.) (G) Average laterality index from corner test behavior of mice before and after MCAO that received nose drops of rmVEGFD (n = 7) or vehicle (n = 8). D, one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s correction for multiple comparisons; E, unpaired t test and two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s correction for multiple comparisons; G, unpaired t test. *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001. Plotted data show mean ± SEM and individual values.