Figure 1: LRRTM4 localizes to GABAergic synapses at mouse retinal rod bipolar axon terminals.
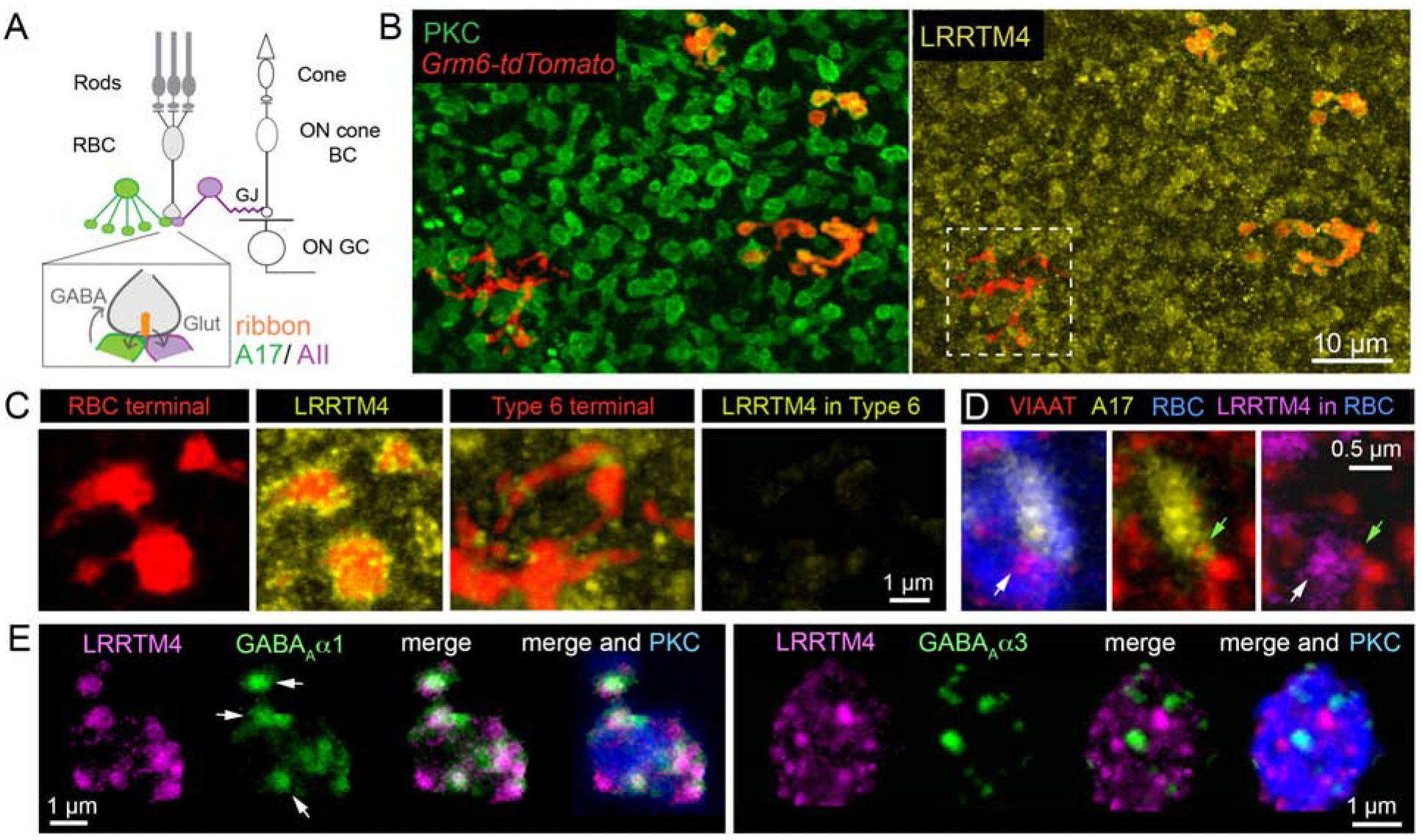
(A) Schematic of retinal pathways. Rod and cone photoreceptors relay light-evoked signals to rod and cone bipolar cells, respectively. Cone photoreceptors synapse onto cone bipolar cells (cone BCs), which connect to retinal output neurons, the ganglion cells (GCs). Rod bipolar cells (RBCs) make glutamatergic (Glut) ribbon synapses onto AII and A17 amacrine interneurons. GABAergic A17 amacrine provide feedback inhibition onto the RBC terminals from which they receive excitatory input. AII glycinergic amacrines form gap-junctions (GJ) with depolarizing (ON) cone BCs thus relaying rod signals to the GCs. (B) En face images show LRRTM4 immunofluorescence selectively localized at protein kinase C (PKC)-positive RBC terminals and not at Type 6 ON cone BC terminals (white box). RBCs and ON cone BCs both express tdtomato in the Grm6-tdtomato transgenic line. (C) Higher magnification view of RBC and Type 6 BC terminals with LRRTM4 immunolabeling. (D) LRRTM4 at RBC terminals (white arrow) is apposed to a VIAAT-immunopositive (green arrow) A17 bouton. (E) LRRTM4 within PKC positive RBC boutons colocalizes with GABAAα1 receptor puncta (arrows, Left panel), but not with GABAAα3 receptor puncta (Right panel).
