Figure 3: Dyad synapse arrangements at rod bipolar cell terminals are perturbed in the absence of LRRTM4.
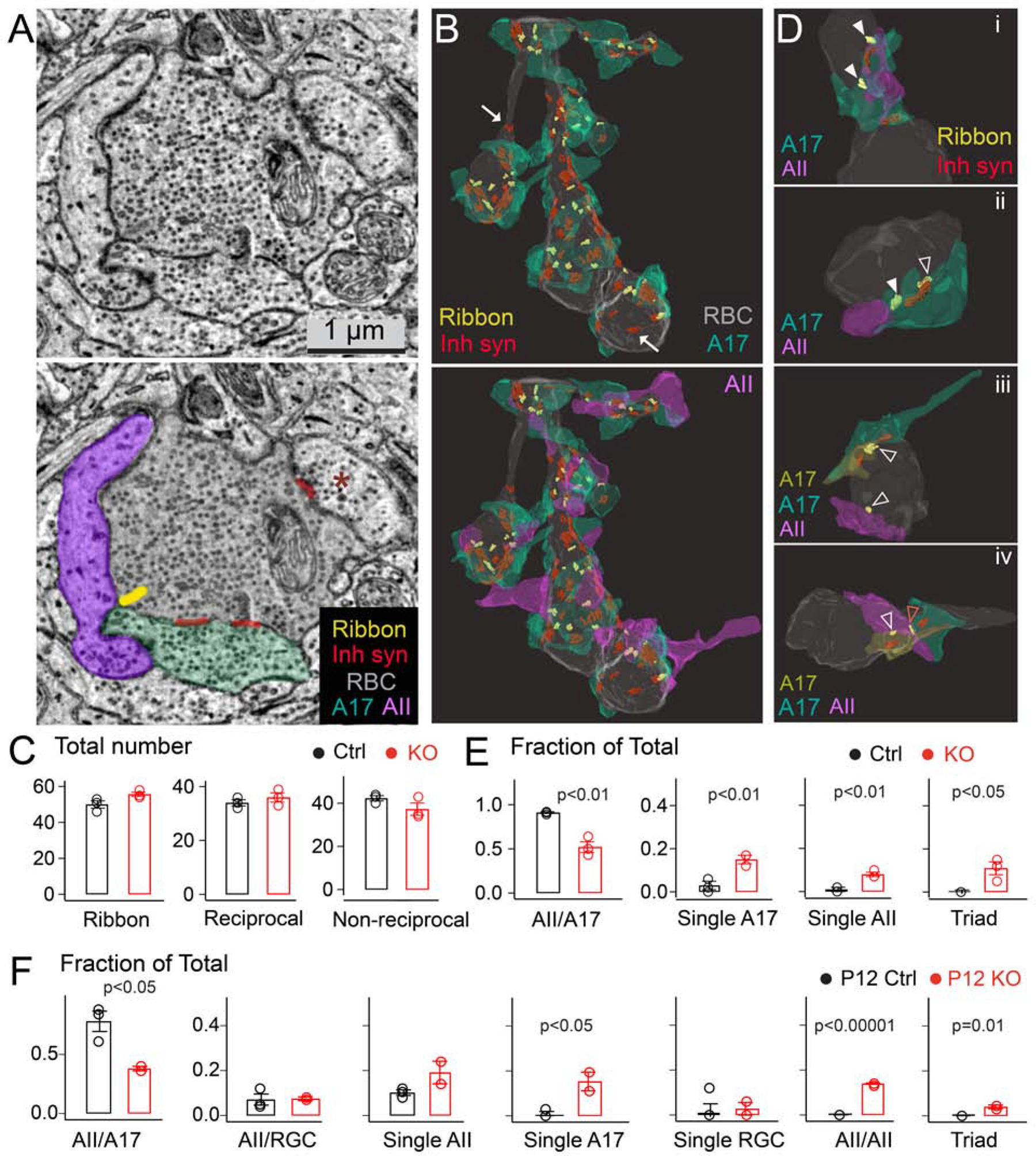
(A) Electron micrograph of the RBC terminal (top: raw image, bottom: pseudocolored) with locations of ribbons, inhibitory synapses (Inh synapse), A17 and AII output partners annotated. Non-A17 inhibitory input on the terminal is marked with a red asterisk. (B) Top: 3D reconstruction of a RBC terminal with ribbons, sites of inhibitory input and A17 boutons. Bottom: 3D view of the same terminal with both dyad partners shown at every ribbon site. Arrows point to non-reciprocal inhibitory sites. (C) Quantification of total number of ribbon synapses, A17 reciprocal synapses, and non-reciprocal inhibitory synapses in adult littermate control (Ctrl) and LRRTM4 knockout (KO) RBC terminals. (N=3 Ctrl, 3 LRRTM4 KO RBC reconstructions from 2 pairs of adult animals). (D) Examples of normal dyad arrangements (solid white arrowheads) in Ctrl (panel i) and mis-arrangements of dyad synapses in LRRTM4 KO RBC terminals (panels ii-iv; open white arrowheads; ‘Triad’ indicated by a red open arrowhead). (E) Fraction of total RBC ribbon sites with the indicated synapse arrangement in Ctrl and LRRTM4 KO terminals. (N=3 Ctrl, 3 KO reconstructions from 2 pairs of adult animals). (F) Fraction of total RBC ribbon sites with the indicated synapse arrangement in P12 terminals. (RGC: retinal ganglion cell, N=3 P12 Ctrl, 2 KO P12 RBC reconstructions). P values listed; two-tailed unpaired T-test across genotypes.
