Figure 3.
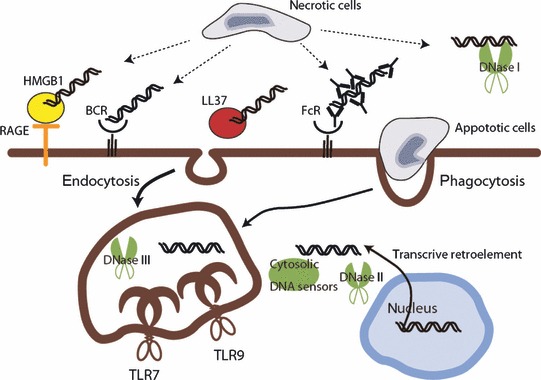
Self‐nucleic acid recognition mechanisms and degradation of DNA. Self‐nucleic acids, which are produced from necrotic or apoptotic cells, are internalized via several pathways and induce innate immune responses. Extracellular DNA is degraded by DNase I, but some of this escapes from degradation by binding to intermediate proteins, such as autoantibodies, LL37, or HMGB1. DNA–protein complexes facilitate internalization through the endocytosis pathway by binding to specific mediators. DNase II plays a role similar to DNase I after self‐DNA internalization or degradation of DNA derived from phagocytosed apoptotic cells in the macrophage. DNase III degrades intracellular DNA derived from the retro element from genomic DNA, which is likely to prevent activation of the cytosolic DNA sensor.
