Figure 1.
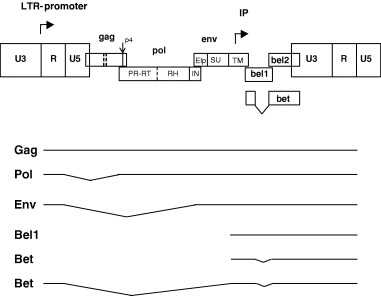
Genetic map and transcription pattern of FVs shown schematically for FFV. The FFV genes gag, pol, env, bel1, and bel2 are depicted as boxes. Sites of proteolytic processing of the precursor proteins are marked by solid and dashed lines. FV PR‐mediated processing results in the Gag p4 peptide and the Pol‐derived PR‐RT, RNase H (RH), and integrase (IN) proteins. The Env precursor is processed by cellular proteases into the novel N‐terminal Env leader protein (Elp) and the SU and TM products. The regulatory long terminal repeats (LTR) are subdivided into the U3, R, and U5 regions (not in scale). The bel 3 gene unique for HFV is not shown. The promoter in the 5′ LTR and the internal promoter (IP) are marked by rectangular arrows pointing into the direction of transcription. The Bet protein consists of Bel1 and Bel2 domains as schematically shown. Below, the LTR‐derived Gag‐, Pol‐, Env‐ and Bet‐encoding transcripts and the IP‐directed Bel1 and Bet mRNAs are schematically shown. Note that a spliced Pol mRNA and the IP transcripts are unique features of FVs. Splicing of the RNAs is indicated by thin broken lines.
