Figure 3.
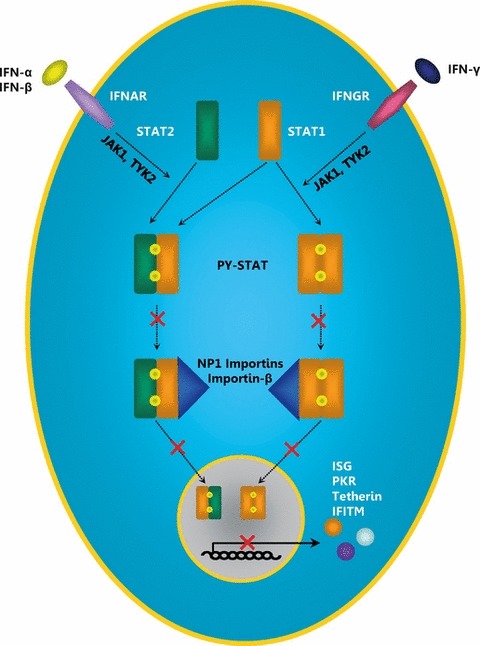
Inhibition of type I and type II IFN signalling by Ebola virus VP24. Upon binding to their receptors, IFNs induce the homo‐ or heterodimerization of STAT1 and STAT2, leading to autophosphorylation of these transcription factors. Exposition of a nuclear localization signal in the phosphorylated STAT proteins (PY‐STAT) allows binding of NP‐1 importins and importin‐β and subsequent nuclear translocation that results in the expression of ISGs. VP24 interferes with the binding of PY‐STAT to NP‐1 importins. PY‐STAT cannot be imported into the nucleus, and the expression of ISGs is suppressed. IFN, interferon; ISG, IFN‐stimulated gene; IFNAR, IFN‐α receptor; IFNGR, IFN‐γ receptor; JAK1, Janus‐activated kinase 1; TYK2, tyrosine kinase 2; STAT, signal transducer and activators of transcription; PY‐STAT, phosphorylated STAT; ISG, IFN‐stimulated gene; PKR, dsRNA‐dependent protein kinase; IFITM, IFN‐induced transmembrane protein.
