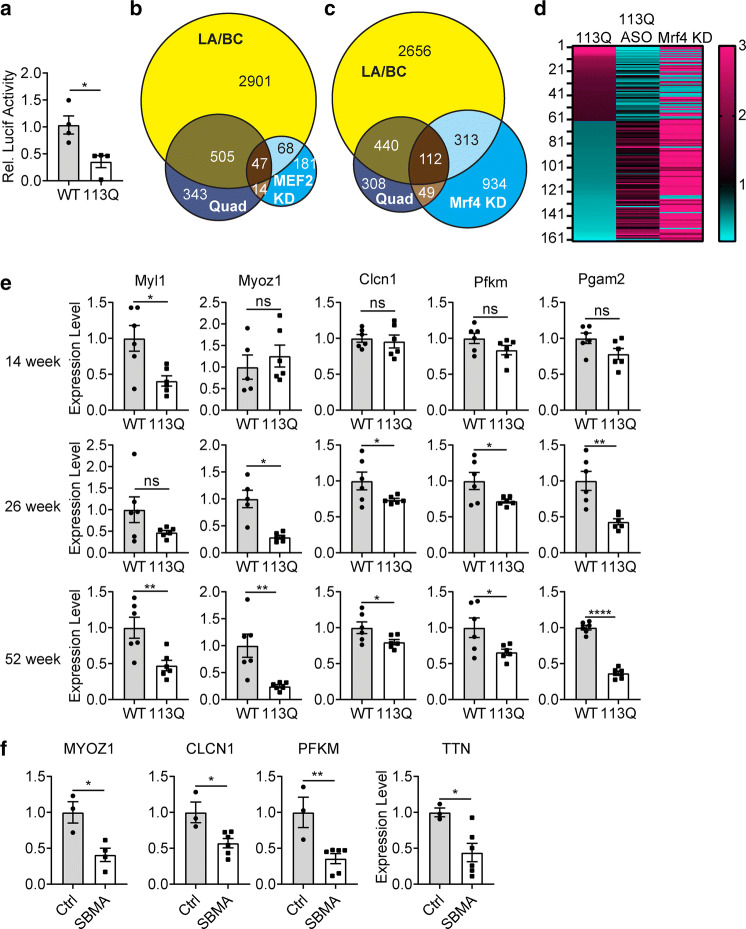
Fig. 4.
Diminished MEF2 activity in AR113Q muscle. a Tibialis anterior of 26-week WT and AR113Q mice were co-transfected with MEF2-luciferase and constitutively expressed Renilla luciferase. MEF2-luciferase activity was measured and normalized to renilla luciferase activity (n = 4/group). Data are mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05 by unpaired t test. b Differentially expressed genes (AR113Q vs WT) from 14 week LA/BC and quadriceps of AR113Q mice were compared to a published set of MEF2 target genes identified by gene knockdown (KD) and validated by ChIP-exo in C2C12 cells. p = 6.21e26 by hypergeometric test for Quad overlap with MEF2 KD and p = 2.67e27 by hypergeometric test for LABC overlap with MEF2 KD. c Differentially expressed genes (AR113Q vs WT) from 14 week LA/BC and quadriceps of AR113Q mice were compared to a published set of gene expression changes downstream of knockdown of Mrf4, a MEF2 repressor protein, in rat tibialis anterior at 6 weeks of age. p = 2.12e−68 for LABC overlap with Mrf4 KD and p = 5.20e−36 for Quad overlap with Mrf4 KD d Heatmap showing fold change of 161 overlapping genes between AR113Q Quad and Mrf4 KD. Three comparisons to WT are displayed: AR113Q Quad, AR113Q Quad from mice treated with antisense oligonucleotides, and tibialis anterior from WT mice following Mrf4 KD. e Relative expression of MEF2 targets PFKM, Ryr1, Myl1, CLCN1, Myoz1 and PGAM2 was measured in WT and AR113Q mice at 14 (left), 26 (middle), and 52 (right) weeks in quadriceps (n = 5–6/group). f SBMA patient and control (Ctrl) muscle biopsies were examined for expression of MEF2 targets CLCN1 (n = 3v6), Myoz1 (n = 3v4), PFKM (n = 3v6), and TTN (n = 3v6) by qPCR. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001 by unpaired t test