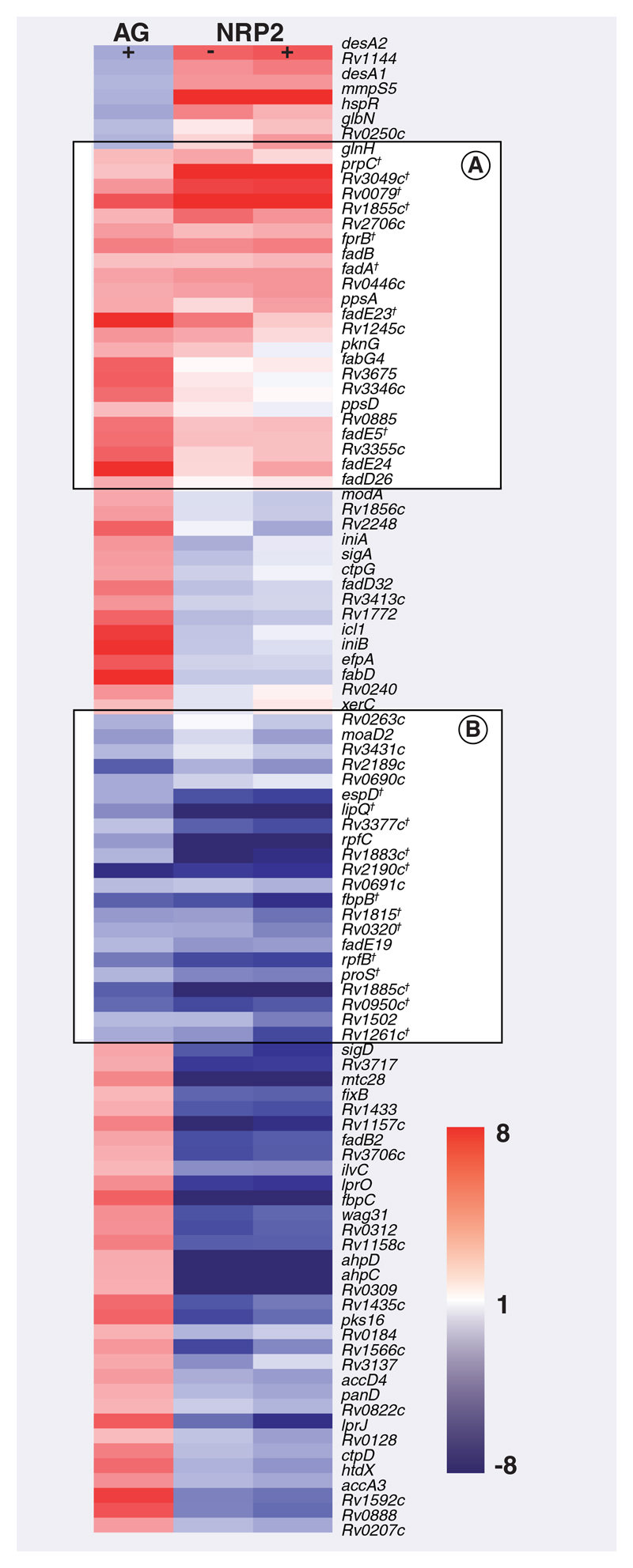
Figure 6. Expression pattern of isoniazid-responsive genes in log-phase and NRP2 bacilli ± isoniazid relative to drug-free log-phase bacilli.
A total of 100 genes, identified as significantly differentially regulated after isoniazid (INH) exposure in AG conditions, were clustered alongside the NRP2 transcriptional profiles. (A & B) show genes induced or repressed after INH exposure and transition to NRP2 compared with untreated log-phase bacilli. Genes are displayed as rows and growth conditions ± INH as columns. Red: induction; blue: repression relative to log-phase drug-free control.
†Genes significantly differentially expressed in both drug-free NRP2 and INH-treated AG bacilli compared with untreated log-phase bacilli.
AG: Aerobic; NRP: Nonreplicating persistence.