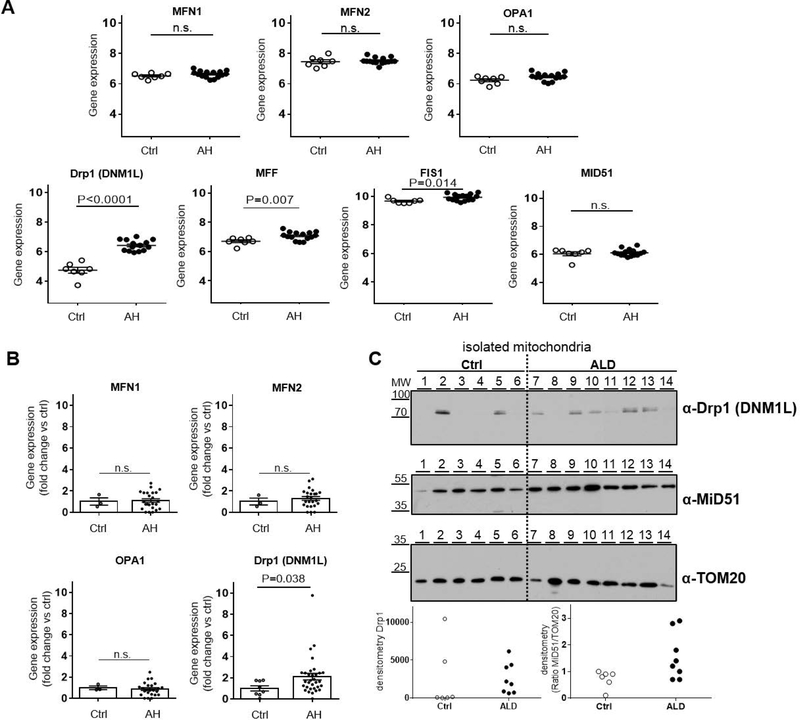
Figure 1. Hepatic expression and activation of the mitochondria-shaping proteins involved in mitochondrial fragmentation are induced during alcoholic hepatitis.
(A) Hepatic gene expression assessed by DNA microarray in liver biopsies from patients with alcoholic hepatitis (AH, n=15) and healthy controls (Ctrl, n=7); GEO reference series GSE28619. Fusion pathway: Mitofusin-1 (MFN1), Mitofusin-2 (MFN2), Optic-atrophy-1 (OPA1) expression was found no different between AH and Ctrl (mean ± SEM; n.s. P>0.05). Fragmentation pathway: Dynamin-1-like protein(Drp1 gene name DNM1L) and its adapters/receptors Mitochondrial fission factor (MFF) and Mitochondrial fission 1 protein (FIS1), but not Mitochondrial dynamics protein of 51KDa (MiD51), were significantly induced in AH (mean ± SEM; P<0.05, n.s. P>0.05).
(B) Hepatic gene expression assessed by RT-PCR in liver biopsies from patients with alcoholic hepatitis (AH, n=32) admitted at the Hospital Clinic of Barcelona, see Table 2 for baseline characteristics, and healthy controls (Ctrl, n=8). Fusion pathway: mRNA levels of MFN1, MFN2 and OPA1 shown no difference between livers of AH and Ctrl (n=3) (mean ± SEM; n.s. P>0.05). Fragmentation pathway: mRNA levels of Drp1 (gene name DNM1L) were increased in AH patients compared to Ctrl (n=8) (mean ± SEM; P<0.05).
(C) Protein analysis in alcoholic hepatitis patients (AH, n=8) admitted at the Clinique d’Hépatologie, Brussels, see Table 3 for baseline characteristics and healthy controls (n=6). Mitochondria isolated from liver tissue of healthy controls (lines 1–6) and AH patients (lines 7–14) were subjected to Western blot analysis (representative pictures, TOM20 as loading control and densitometry of Drp1 and ratio MiD51/TOM20, individual values). Drp1 was found increased in the mitochondrial fraction of the majority of AH samples compared to ctrl.