Figure 1. The F-RAM and N-RAM Reporters Selectively Capture Fos- and Npas4-dependent Neuronal Ensembles.
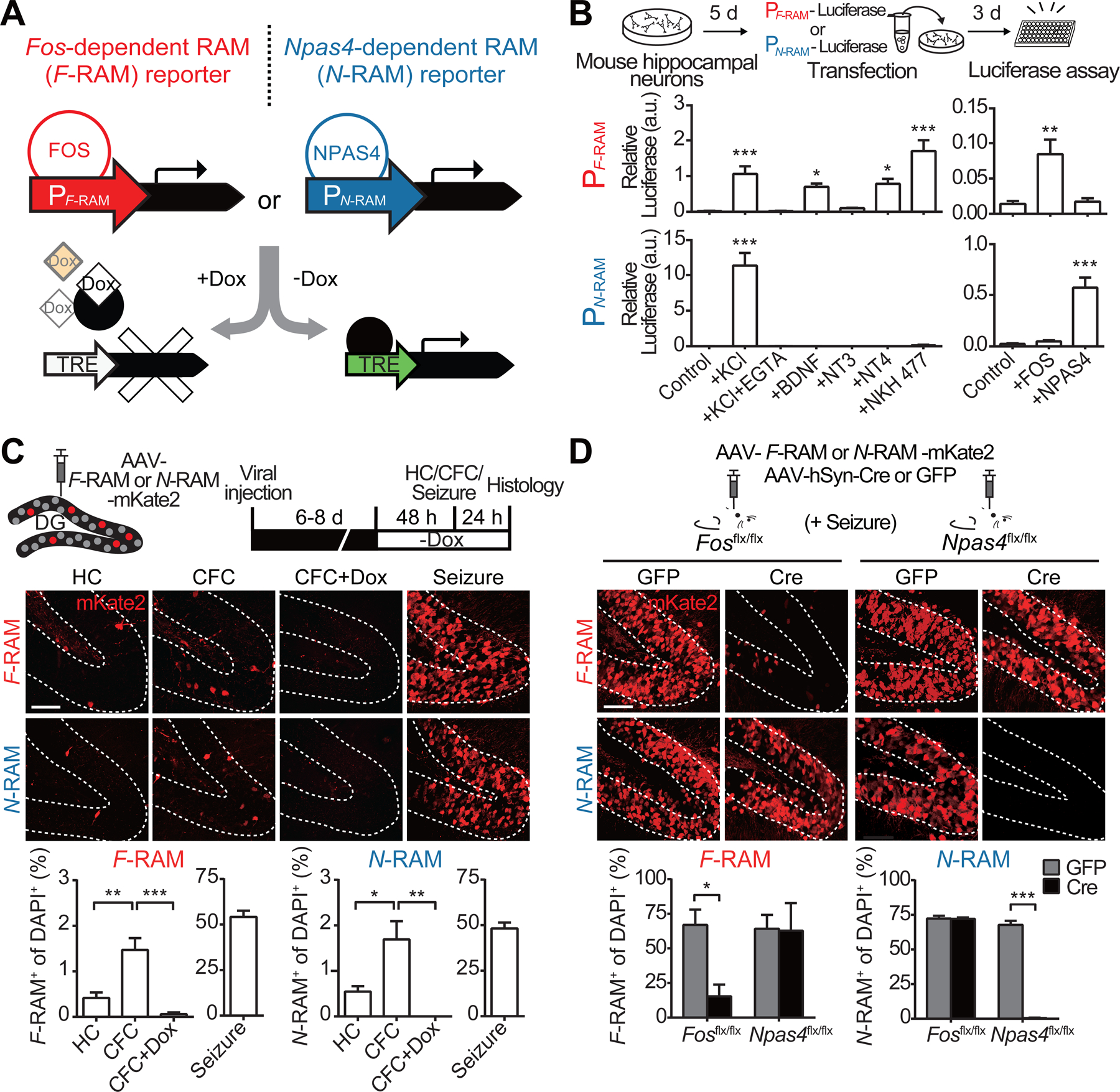
(A) Design of the F-RAM and N-RAM reporters.
(B) Characterization of PF-RAM and PN-RAM. Cultured hippocampal neurons were transfected with luciferase expression plasmids and treated with various extracellular stimuli. The induction of PF-RAM or PN-RAM by various extracellular stimuli was measured by luciferase assay. One-way ANOVA, Dunnett’s test, n = 8–9.
(C) F-RAM and N-RAM label experience-activated neuronal ensembles in vivo. Representative images of the dorsal DG granule cell layers (GCL, dashed lines) and quantifications showing ensembles labeled under the home cage (HC), contextual fear conditioning (CFC), CFC but on Dox (CFC+Dox), and seizure conditions. One-way ANOVA, Tukey’s test, n = 4 per condition.
(D) F-RAM and N-RAM are dependent on endogenous Fos and Npas4, respectively. Representative images and quantifications showing seizure-induced reporter activation in Fos and Npas4 conditional knockout animals. Two-way ANOVA, Sidak’s test, n = 3–4.
