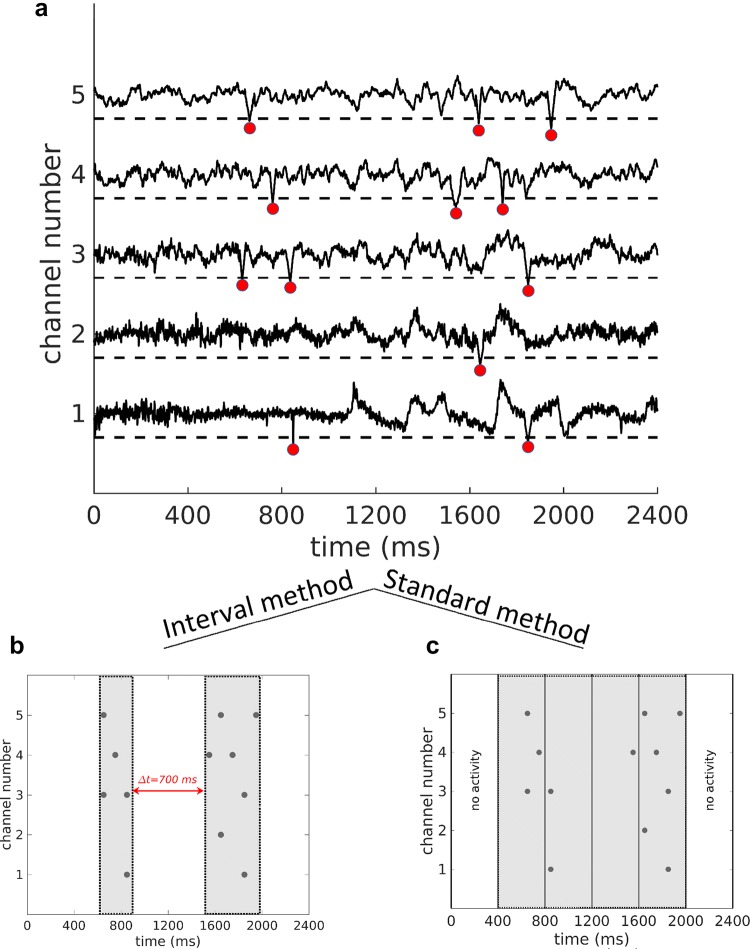
Fig. 1.
Brain activity and definition of avalanches. a EEG time course of five electrodes. Peak time and peak amplitude are extracted from suprathreshold negative (or positive) EEG deflections that cross a constant threshold set at a multiple of the EEG SD (all here were negative). Schematic highlighting differences in avalanche identification using b the interval method and c the standard method. The standard method identifies one avalanche based on four consecutive active bins, whereas the interval method identifies two avalanches based on two events exhibiting a time interval > 400 ms