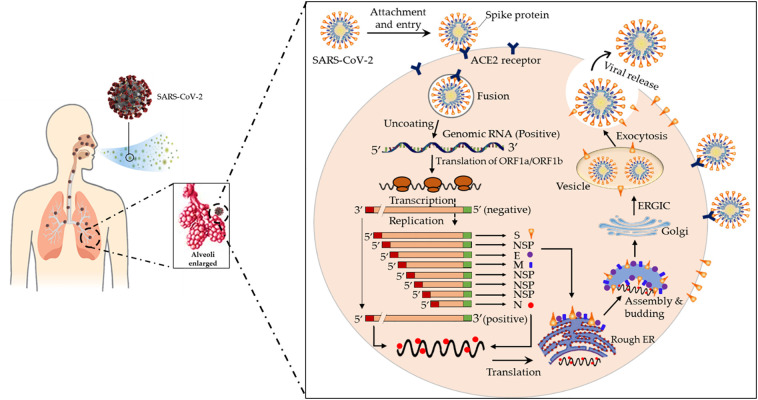
Fig. 2.
The life cycle of SARS-CoV-2 in human lung cells. Coronavirus is most often transmitted by droplets while sneezing and coughing and its journey begins in the first days after infiltration from the upper respiratory tract. The spike proteins of SARS-CoV-2 binds to ACE2 receptors. The virion then releases RNA genome into the cell and translation of structural and non-structural proteins follows. ORF1a and ORF1ab are translated to produce pp1a and pp1ab polyproteins, which are cleaved by the proteases that are encoded by ORF1a to yield non-structural proteins. This is followed by assembly and budding into the lumen of the ERGIC. Virions are then released from the infected cell through exocytosis (Adnan Shereen et al., 2020). NSP, non-structural proteins; ACE2, Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2; Rough ER, Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum; ERGIC, Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Intermediate Compartment.