Figure 1.
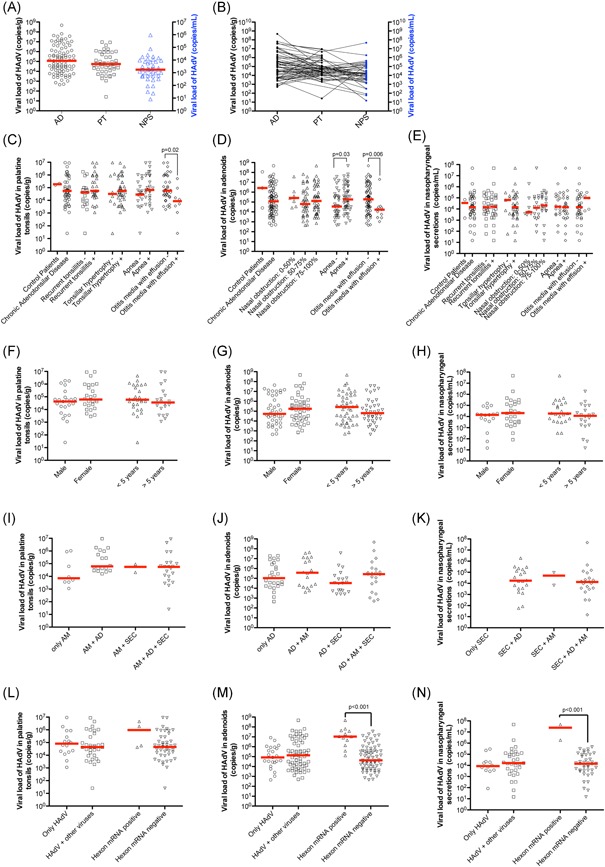
Viral load of HAdV in adenoids, palatine tonsils, and nasopharyngeal secretions by qPCR. A, HAdV viral loads in ADs, PTs, and NPS from patients with adenotonsillar chronic diseases. B, Patterns of HAdV viral loads in patients with simultaneous detection in several sites. The viral loads in the same patient were connected by a straight line. C, HAdV viral loads in palatine tonsils in the different clinical conditions. D, HAdV viral loads in adenoids in the different clinical conditions. E, HAdV viral loads in NPS in the different clinical conditions. F, HAdV viral loads in palatine tonsils according to sex and age. G, HAdV viral loads in adenoids according to sex and age. H, HAdV viral load in NPS according to sex and age. I, HAdV viral loads in palatine tonsils from patients with this virus detectable only in this tissue or when the agent was also detectable in other sites, including as adenoids and NPS. J, HAdV viral loads in adenoids from patients with this virus detectable only in this tissue or when the agent was also detectable in other sites, such as palatine tonsils and NPS. K, HAdV viral loads in NPS from patients with this virus detectable only in this site or when the agent was also detectable in other tissues, including adenoids and palatine tonsils. L, Association of HAdV viral loads in palatine tonsils with the presence of viral coinfection or with the detection of the mRNA of the HAdV hexon gene. M, Association of HAdV viral loads in adenoids with the presence of viral coinfection or with the detection of the mRNA of the HAdV hexon gene. N, Association of HAdV viral loads in NPS with the presence of viral coinfection or with the detection of the mRNA of the HAdV hexon gene. The red line in all graphs represents the median of the viral load in the analyzed condition. ADs, adenoids; HAdV, human adenovirus; NPS, nasopharyngeal secretions; PTs, palatine tonsils; qPCR, quantitative real‐time PCR
