Figure 1.
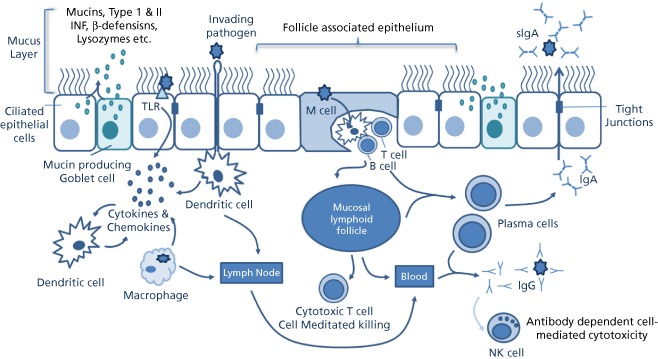
The epithelial barrier is composed of ciliated pseudo‐stratified columnar epithelial cells joined by tight junctions, mucus containing a range of antimicrobial agents traps pathogens that are transported out of the airways by cilia beating. Mucosal epithelial cells detect pathogens using pattern recognition receptors and signal to epithelial DCs via cytokines and chemokines. DCs beneath the epithelium extend dendrites between epithelial cells to sample the lumen. In the FAE of the MALT, M‐cells transport antigen to DCs residing in M‐cell pockets, which present antigens to intraepithelial T and B lymphocytes. Activated DCs migrate to lymphoid follicles or nodes to initiate adaptive immune responses. Plasma cells migrate from the lymphoid follicles and produce IgA, which is transported across the epithelium into the lumen.
