Figure 2.
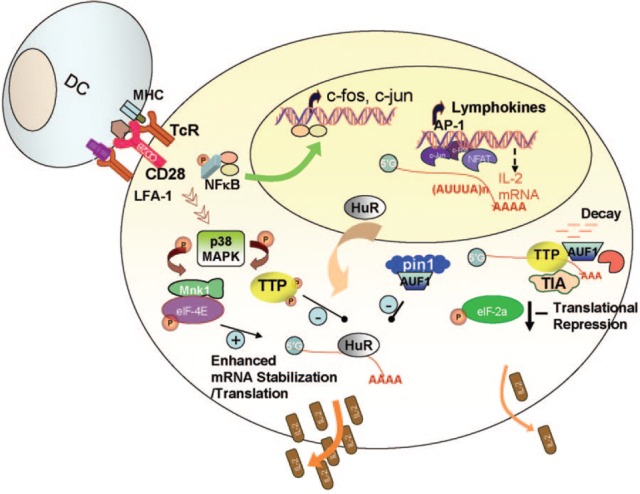
Enhanced mRNA stabilization and translation in T cell activation. APCs, like DC, present antigens efficiently within MHC to T cells through interaction with TcR. Facilitated by other costimulatory molecules, T cell activation occurs, resulting in induction of immediate early response gene products such as c‐fos and c‐jun. These, as AP‐1 complex, with NFAT activate the IL‐2 promoter. Costimulatory molecules, such as CD28 and LFA‐1 on T cells, transduce signals, which also trigger mRNA stabilization and other post‐transcriptional effects. For example, HuR translocates from the nucleus to the cytoplasm and stabilizes ARE‐mRNAs, and pin1 isomerizes another RNA‐binding protein, AUF1, leading to loss of its mRNA decay‐promoting function. These events contribute to early and rapid response of T cell activation and cytokine production. In later phase, shut‐off also can be facilitated by post‐transcriptional mechanisms including mRNA destabilization and translational arrest. Details are given in the text. pin1, Peptidyl‐prolyl isomerase; TIA, T cell intracellular antigen.
