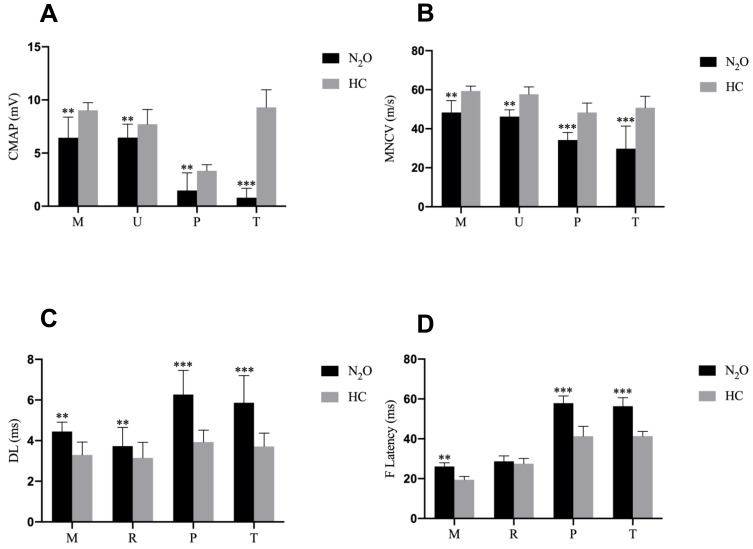
Figure 1.
Motor nerve conduction study results in the health control (HC) and N2O abuse groups. (A) The compound muscle action potential amplitude, (B) motor conduction velocity, (C) distal latency, and (D) F-wave latency of each motor nerve for the HC (grey bar) and N2O-abuse (black bar) groups.
Notes: Data are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean. Significant difference is indicated by **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.
Abbreviations: M, median nerve; U, ulnar nerve; P, peroneal nerve; T, tibial nerve.