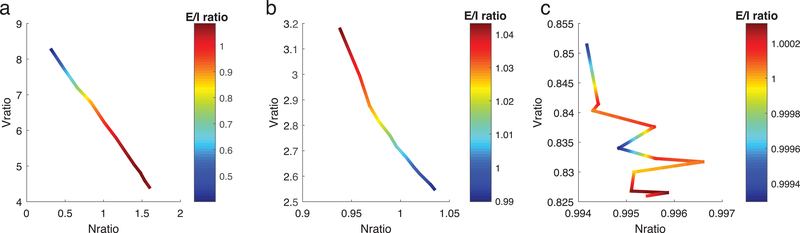
Figure 7.
The contribution of changes in E and I firing rates (Nratio) and excitatory and inhibitory synaptic current driving forces (Vratio) to changes in E/I ratio. Values for wE are fixed near each balanced state (a: first crossing, b: second crossing, c: third crossing) and frequency of noise events to E cells is increased to vary E/I ratio (color of curves). Curves show relationships between values of the ratio of E to I cell average firing rates (Nratio, x-axis) and values of the ratio of differences between average membrane potentials and reversal potentials of the excitatory and inhibitory synaptic currents (Vratio, y-axis) at each value of E/I ratio. At the first crossing (a), increasing E/I ratio mirrors increasing Nratio while at the 2nd crossing it mirrors increasing Vratio.