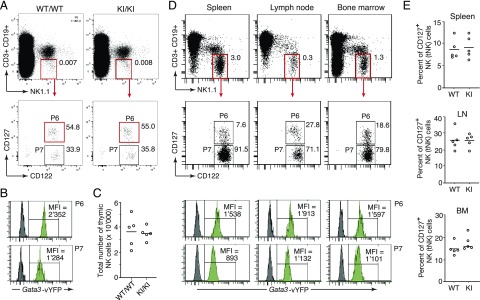
FIGURE 4.
Monitoring Gata3 expression in thymic versus conventional NK cell subsets. (A) Gating strategy for flow cytometric discrimination of tNK (gate P6) and cNK cells (gate P7) based on differential IL-7R (CD127) expression. Dot plots show total thymocytes from C57BL/6 wild-type (WT) (WT/WT) and homozygous GATIR knock-in (knock-in [KI]/KI) mice. (B) Representative histograms showing significantly increased Gata3-vYFP reporter expression in tNK (gate P6) versus cNK (gate P7) cells from the thymus of a homozygous GATIR mouse (green histograms). Dark gray histograms represent corresponding cell populations from a WT control mouse. The histograms are derived from the same cells shown in the gating scheme above. (C) Thymi from homozygous GATIR mice (KI/KI) have similar tNK cell numbers as WT (WT/WT) C57BL/6 control mice. Each circle represents data from one individual mouse. (D) Top panels show gating scheme to discriminate tNK (gate P6) and cNK (gate P7) cell subsets in spleen, lymph node (LN), and BM from a representative homozygous GATIR mouse. The green histograms below show Gata3-vYFP reporter expression in the respective tNK or cNK cell subset. Dark gray histograms represent corresponding cell populations from a WT control mouse. (E) Homozygous GATIR (KI) and C57BL/6 WT control mice (WT) have similar frequencies of tNK cells (CD127+ NK cells) in spleen, LN, and BM. Each circle represents data from one individual mouse (in total, five mice of each genotype were analyzed). Gating for CD127+ NK cells (tNK cells) as shown in (D).