FIG 5.
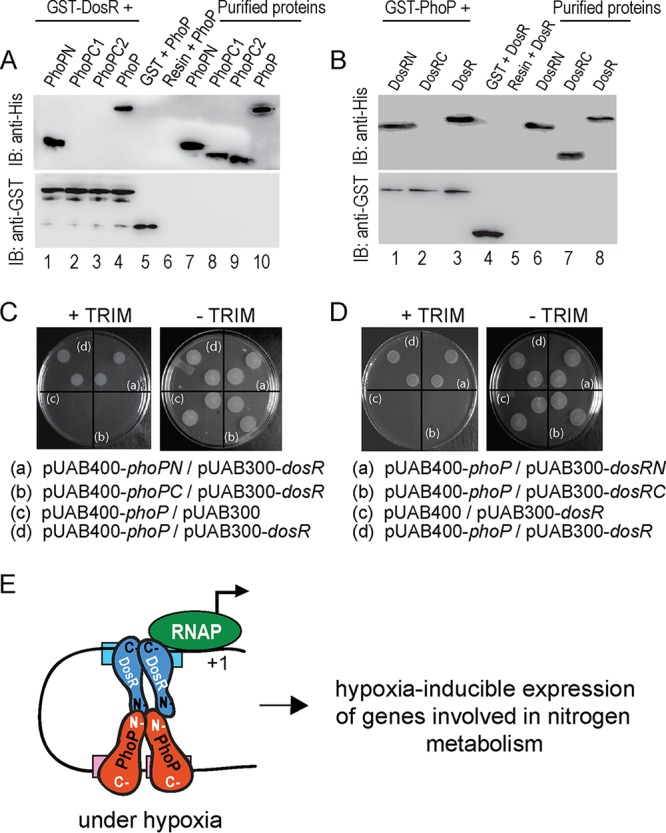
Probing interacting domains of PhoP and DosR. (A) The indicated His6-tagged PhoP domains were incubated with glutathione-Sepharose, previously immobilized with GST-DosR. Fractions of bound proteins (lanes 1 to 4) were analyzed by anti-His (upper panel) or anti-GST antibody (lower panel). Control sets include GST alone (lane 5) or the resin alone (lane 6); lanes 7 to 10 resolve purified PhoP constructs. (B) Likewise, indicated His6-tagged DosR domains were incubated with glutathione-Sepharose previously immobilized with GST-PhoP. Fractions of bound proteins (lanes 1 to 3) were probed with anti-His or anti-GST antibody (as described above). Control sets include GST alone (lane 4) or the resin alone (lane 5); lanes 6 to 8 resolved purified DosR constructs. The results suggest that DosRN and not DosRC retains the ability to interact with PhoP. (C and D) M-PFC experiments examined interactions between the indicated PhoP domains and DosR (C) or between PhoP and indicated DosR domains (D), respectively, using the full-length PhoP/DosR pair as the positive control. (E) Model depicting how PhoP and DosR function as coactivators of hypoxia-inducible gene expression (right). While PhoP-DosR interaction via their received domains contributed to the additional stability of the transcription initiation complex, mycobacterial RNA polymerase bound to the target site of the promoter to initiate transcription.
