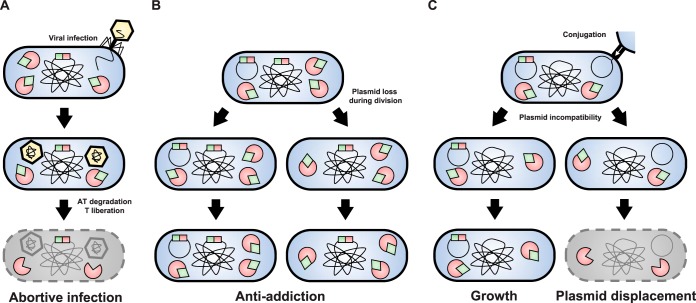
FIG 2.
Roles of TA systems regarding mobile genetic elements. TA genes, as well as proteins, are represented in red (toxins) and green (antitoxins). (A) Protection against phages. Some TA systems have been shown to contribute to viral defense through a process known as “abortive infection.” Viral infection would lead to a molar excess of toxin over its cognate antitoxin by yet-unknown mechanisms, leading to the killing of infected cells, preventing phage replication and propagation. (B) Antiaddiction. Chromosomal homologs of plasmid-encoded TA systems can cross-neutralize their toxic activities. Therefore, failure to inherit a TA-encoding plasmid will not lead to postsegregational killing if a homologous TA system is encoded on the chromosome. (C) Plasmid displacement. Cells that acquire more than one plasmid from the same incompatibility group through conjugation will partition these plasmids in different daughter cells. If one of such plasmids encodes a TA system, cells that fail to inherit this plasmid will still contain TA proteins in its cytoplasm and will be killed by postsegregational killing.