Figure 1.
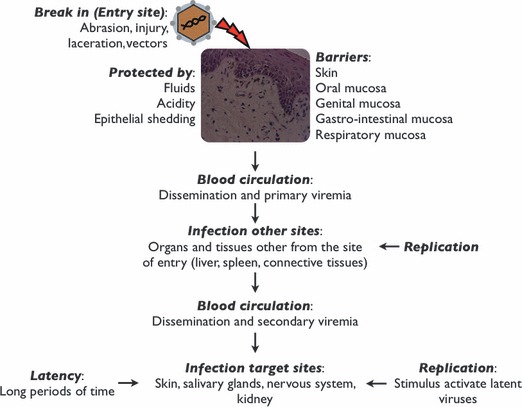
Viral infection steps: entry, replication, dissemination and infection of target cells/organs. Virions enter the host organism and spread to target tissues/organs where they can replicate and/or cause a persistent infection (latency). Latent viruses can become reactivated by several immune‐compromising events, such as smoking, inflammation, stress, trauma and immunosuppressive diseases.
