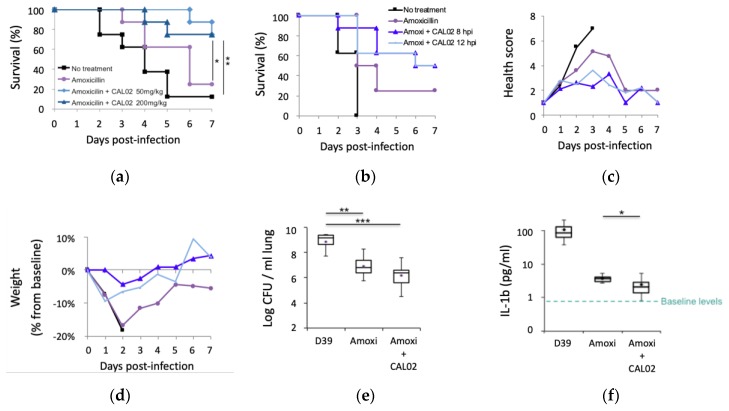
Figure 3.
CAL02 in addition to antibiotics in acute pneumonia caused by S. pneumoniae. CD-1 mice were challenged with a lethal intranasal infection of S. pneumoniae D39. A single dose of amoxicillin (0.2 mg/kg in (a–d), 1 mg/kg in (e,f)) was administered subcutaneously at 4 h post-infection. Study (a): A single dose of CAL02 (50 or 200 mg/kg) was administered intravenously at 4 h post-infection. Study (b): A single dose of CAL02 (50 mg/kg) was administered intravenously at 8 or 12 h post-infection. At the end of the study, all surviving mice treated with CAL02 had fully recovered as indicated by health scores(c) and weight (d). (e,f) Impact of CAL02 (200 mg/kg) administered 6 h after antibiotics on bacterial loads in lungs (e) and on blood IL-1beta (f), measured at 30 h post-infection; (a–e) n = 8 per group; (f) n = 4 in the untreated group; and n = 8 in treated groups. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.005; Log-rank (Mantel–Cox) test p < 0.05. [25].