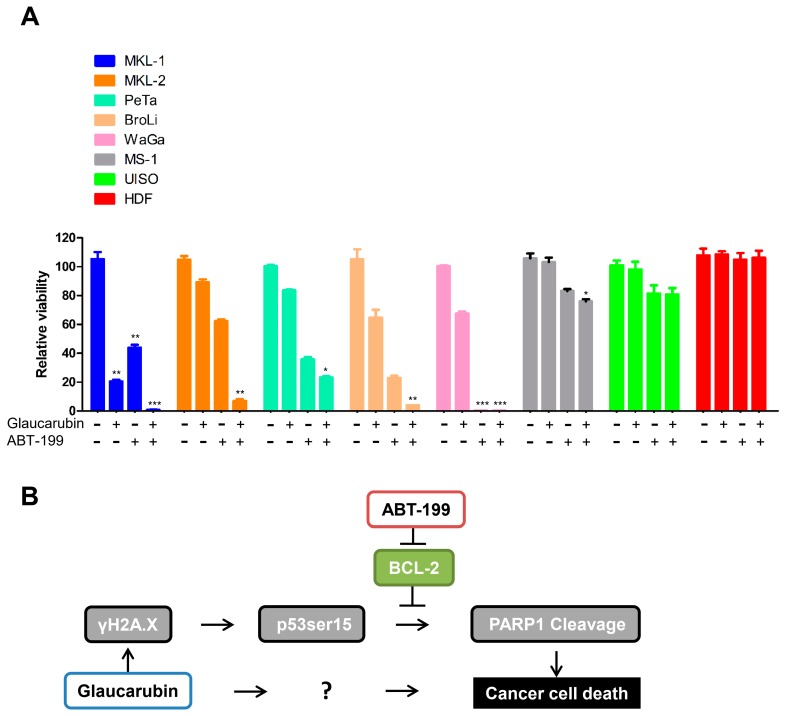
Figure 6.
Targeting BCL2 function using an FDA approved inhibitor to achieve better killing of MCC cells. (A) Cell viability assay of MCC cells and primary HDFs treated with DMSO or the indicated concentrations of glaucarubin, ABT-199, or both for 72 h at 37 °C in 5% CO2. An asterisk (*) signifies the number of standard deviations from the mean. P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001. (B) Proposed working schematic of effects induced by glaucarubin in MCPyV-positive MCC cell lines. MCCs can develop resistance to this cell death pathway by failing to repress BCL-2. Inhibition of BCL-2 by ABT-199 can circumvent this resistance mechanism. The question mark denotes an unknown mechanism underlying the sensitivity of MCPyV-positive MCC cells to glaucarubin.