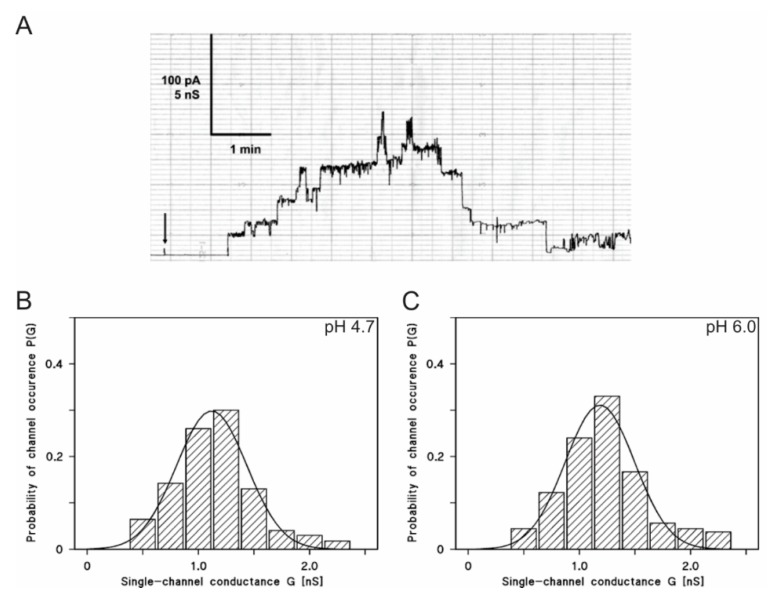
Figure 9.
Pore-forming activity of LtxA in asolectin/n-decane membranes at different pH values. (A). Single-channel recording of LtxA in an asolectin/n-decane membrane at pH 4.7. Current recording of an asolectin/n-decane membrane, performed in the presence of 10 nM LtxA added to the cis-side of the membrane. The aqueous phase contained 1 M KCl, 10 mM MES-KOH, pH 4.7. The applied membrane potential was 20 mV at the cis-side (indicated by an arrow), at 20 °C. (B). Histogram of the probability P (G) of an occurrence of a given conductivity unit observed for LtxA with membranes formed of 1% asolectin dissolved in n-decane in a salt solution at pH 4.7. The histogram was calculated by dividing the number of fluctuations with a given conductance unit by the total number of conductance fluctuations. The average conductance was 1.1 ± 0.31 nS for 47 conductance steps derived from nine individual membranes. The value was calculated from a Gaussian distribution of all conductance fluctuations (solid line). The aqueous phase contained 1 M KCl, 10 mM MES-KOH, pH 4.7 and 10 nM LtxA; the applied membrane potential was 20 mV at 20 °C. (C). Histogram of the probability P(G) for the occurrence of a given conductivity unit observed for LtxA with membranes formed of 1% asolectin dissolved in n-decane in a salt solution at pH 6.0. The average conductance was 1.20 ± 0.31 nS for 95 conductance steps derived from 17 individual membranes. The aqueous phase contained 1 M KCl, 10 mM MES, pH 6.0 and about 10 nM LtxA; the applied membrane potential was 20 mV at 20 °C.