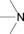
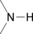
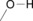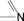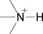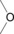Table 1.
Common H‐bonding sites in biomolecules.
|
Acceptor sites |
Donor sites |
||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
amines |
|
water, alcohols, phenols, carboxylic acids |
|
|
imines |
|
amines, amides, azoles |
|
|
nitriles |
|
ammonium ions |
|
|
alcohols, ether, water |
|
|
|
|
amides, esters, ketones |
|
|
|
|
P (phosphine‐) N (amine‐)oxides S (sulfo‐) |
|
|
|
|
Fluorine |
|
|
|
Anions |
RCO2 − : carboxylates RSO3 − : sulfonates ROPO3 2−: phosphates Hal−: halide (fluoride, chloride) |
|
|
This article is being made freely available through PubMed Central as part of the COVID-19 public health emergency response. It can be used for unrestricted research re-use and analysis in any form or by any means with acknowledgement of the original source, for the duration of the public health emergency.