Figure 7.
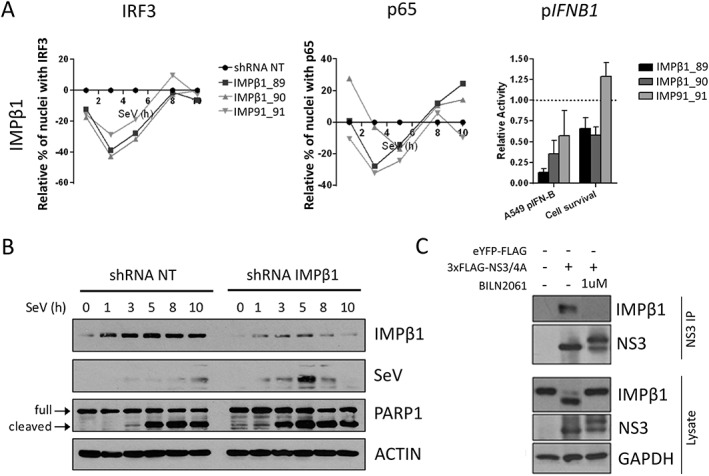
Importin β1 (IMPβ1) silencing impairs IFN regulatory factor 3 (IRF3) and NF‐κB p65 nuclear translocation, IFNB1 induction, and increases Sendai virus (SeV) protein expression and cell apoptosis. A, A total of 3 independent short hairpin RNA (shRNA) targeting IMPβ1 significantly affected nuclear translocation of both IRF3 (left panel) and NF‐κB p65 (middle panel) when compared with the shRNA NT. Relative percentage of cells containing IRF3 and p65 in the nucleus are illustrated after normalization of the control shRNA NT to 0 for all time points. The effect of shRNA‐mediated knockdown on SeV‐induced IFNB1 production is measured in A549 cells stably expressing the firefly luciferase under the control of the IFNB1 promoter (right panel). In addition, the effects of each shRNA on cell proliferation and survival are evaluated using images from the microscopy screen by dividing the total number of nuclei for a given shRNA and dividing it by the total number of nuclei for the shRNA NT control (right panel). B, Immunoblot analysis of A549 cells infected with SeV for 1, 3, 5, 8 or 10 hours following transduction with shRNA NT (control) or shRNA 89 targeting IMPβ1 for 3 days. PARP1 cleavage (arrows) is used as apoptosis readout. C, Human Embryonic Kidney (HEK)293T cells are transfected with 3×FLAG‐NS3/4A expression vector and treated with 1 μM of BILN 2061 PI. At 48 hours post‐transfection, cells are harvested and co‐immunoprecipitation using anti‐FLAG coated beads is performed on cell lysates. NS3 and IMPβ1 interaction is resolved using immunoblot. NS3, NS3/4A precursor, IMPβ1 and cleaved IMPβ1 are resolved using immunoblotting analysis of cell lysates
