Figure 1.
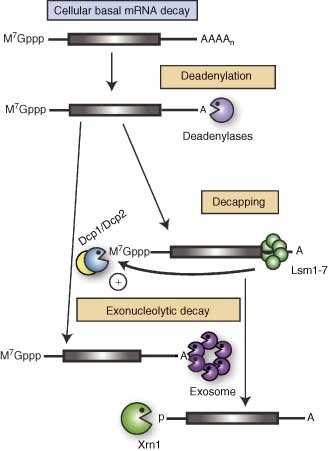
Basal pathways of cellular mRNA decay. Degradation of normal cellular mRNA initiates with removal of the poly(A) tail by one of the cellular deadenylases. Subsequently, the Lsm1–7 protein complex binds the 3′ untranslated region (UTR) of the deadenylated messages and stimulates decapping by the Dcp2 enzyme and its activator protein Dcp1. The message body is subject to 3′→5′ exonucleolytic decay by the exosome or 5′→3′ decay by Xrn1.
