Figure 2.
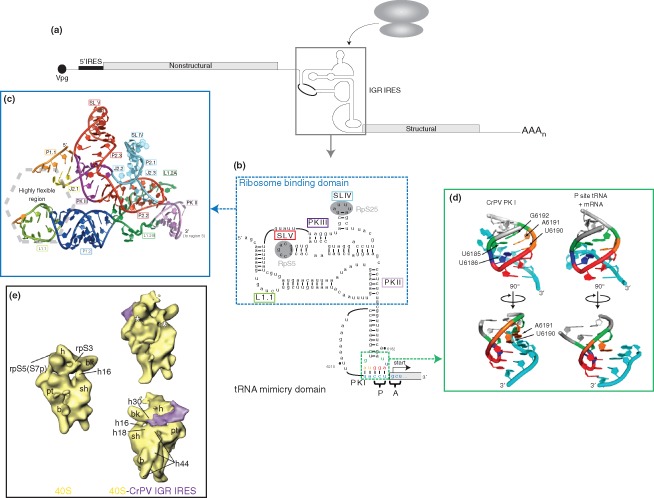
Dicistrovirus intergenic region internal ribosome entry site (IGR IRES). (a) Genome organization of members of the Dicistroviridae family. Dicistroviruses have a single‐stranded, positive‐sense RNA genome that contains the genome‐linked protein (Vpg) and poly(A) tail at the 5′‐ and 3′‐ends, respectively. The genome contains two non‐overlapping open reading frames. The upstream cistron (encoding viral nonstructural proteins) is regulated by the 5′ IRES, while the downstream cistron (encoding viral structural proteins) is expressed under the regulation of the IGR IRES (boxed). The IGR IRES can directly recruit ribosomes in the absence of canonical translation initiation factors. (b) Sequence and secondary structure of the CrPV IGR IRES. The IGR IRES adopts a triple‐pseudoknotted structure (PKI/II/III) with two independently folded domains: the ribosome binding domain (boxed in blue) and tRNA‐mimicry domain. Within the ribosome binding domain, stem‐loop (SL) V interacts with ribosomal protein (RP) S5 whereas SL IV interacts with RPS25 (shaded in gray). The conserved L1.1 bulge is thought to interact with the L1 stalk of the 60S subunit to direct 80S formation. Notable structural elements are boxed in the corresponding colors as those used in crystal structure in (c). The tRNA‐mimicry domain structurally mimics an authentic codon:anticodon interaction and establishes the translational reading frame by occupying the ribosomal P site. IRES‐mediated translation initiates from the A site and at a non‐AUG codon to direct synthesis of the viral structural proteins. The IRES codon:anticodon‐like interaction is boxed in green. Specific nucleotides within this region are depicted in the corresponding colors as the structure shown in (d). (Reprinted with permission from Ref 44. Copyright 2010 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press) (c) Crystal structure of the ribosome binding domain from the Plautia stali intestinal virus. The ribosome binding domain forms a solvent‐inaccessible core that mediates contacts with the 40S ribosomal subunit. (Reprinted with permission from Ref 45. Copyright 2006 American Association for the Advancement of Science) (d) Comparison of the CrPV PKI codon:anticodon‐like interaction and an authentic P‐site mRNA:tRNA interaction. Analogous bases in both structures are highlighted in the same color. (Reprinted with permission from Ref 46. Copyright 2008 Nature Publishing Group) (e) Cryo‐EM reconstructions of the vacant human 40S ribosomal subunit (left) and the CrPV IGR IRES‐bound 40S complex (right) at 25.3 Å and 20.3 Å, respectively. The IGR IRES binds to the intersubunit space and induces conformational changes in the 40S subunit (indicated by asterisk). (Reprinted with permission from Ref 47. Copyright 2004 Cell Press)
