Figure 5.
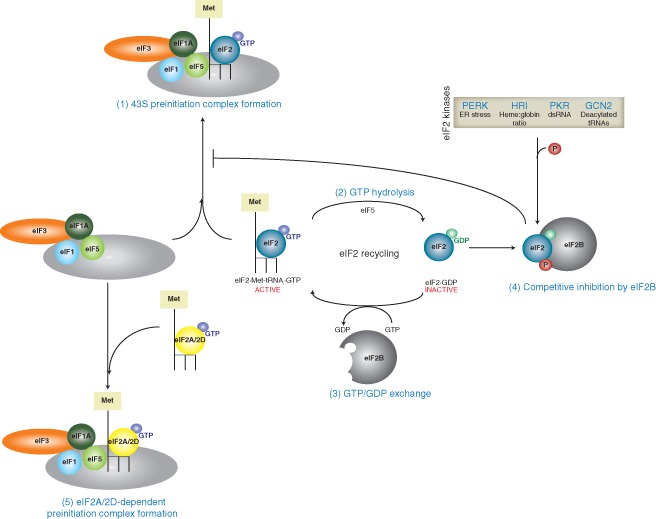
Recycling of eIF2 during translation initiation. During translation initiation, the eIF2·Met‐tRNAi·GTP ternary complex is recruited to the 43S preinitiation complex and is involved in start codon recognition (1). Upon cognate codon:anticodon pairing, eIF5 mediates hydrolysis of eIF2‐bound GTP to GDP (2), which must be recycled by the guanine nucleotide exchange factor eIF2B for subsequent rounds of initiation (3). The α‐subunit of eIF2 is susceptible to phosphorylation by various eIF2α kinases (PERK, HRI, PKR, and GCN2) in response to specific environmental triggers. The phosphorylated form of eIF2α acts as a competitive inhibitor of eIF2B (4), thus preventing recycling of the GDP‐bound eIF2 to the GTP‐bound form and decreasing the availability of the ternary complex pool for translation initiation. Interestingly, some viruses including hepatitis C virus (HCV) and alphaviruses utilize alternate initiation factors such as eIF2A and eIF2D to deliver the initiator tRNA (5). This allows viral translation to proceed when the canonical translation initiation pathway through the eIF2·Met‐tRNAi·GTP ternary complex is compromised.
